PERENCANAAN PROGRAM PMKP RSUD KARAWANG
advertisement

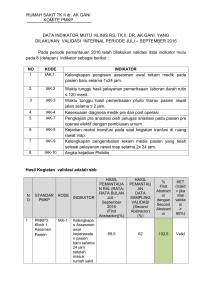
PERENCANAAN PROGRAM PMKP RSUD KARAWANG 1 PEMILIHAN PRIORITAS PROGRAM PMKP (PENINGKATAN MUTU & KESELAMATAN PASIEN) 2 3 Daftar Isi DOKUMENTASI PEMILIHAN PRIORITAS PROGRAM PMKP Daftar isi ................................................................................. Materi bahan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP .................. Indikator area klinis ........................................................... Indikator area manajerial .................................................. Indikator sasaran keselamatan pasien ............................. Indikator Joint Commission International Library .............. Notulen rapat pemilihan prioritas program PMKP ................. Waktu ................................................................................ Jumlah peserta yang diundang ........................................ Jumlah peserta yang hadir ............................................... Materi pembahasan .......................................................... Pembahasan ..................................................................... Kesimpulan ....................................................................... Lampiran ............................................................................... Undangan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP ................. Daftar undangan peserta rapat ......................................... Daftar hadir peserta undangan rapat ................................ Susunan acara ................................................................. Dokumentasi Gambar ....................................................... Halaman i 1 1 3 4 4 8 8 8 8 8 8 14 16 17 19 23 24 4 MATERI BAHAN PEMILIHAN PRIORITAS PROGRAM PMKP 5 Materi Bahan Pemilihan Prioritas Program Peningkatan Mutu dan Keselamatan Pasien (PMKP) Indikator Area Klinis 1. Asesmen Pasien a. Asesmen awal medis lengkap dalam 24 jam pada pasien RI b. Asesmen awal keperawatan lengkap dalam 24 jam pada pasien RI c. Asesmen medis pasien bedah sebelum operasi d. Asesmen medis anestesi sebelum operasi e. Pelaksanaan skrining nutrisional f. Asesmen nyeri pada pasien rawat inap g. Asesmen risiko jatuh pada pasien rawat inap h. Pre visit anestesi i. Pasien stroke yang dilakukan assesmen rehabilitasi medis (International Library) j. Asesmen awal pasien emergency 2. Pelayanan Laboratorium a. Waktu tunggu hasil pelayanan laboratorium b. Pelaksana ekspertisi c. Tidak adanya kesalahan pemberian hasil pemeriksa laboratorium d. Waktu tunggu pemeriksaan laboratorium cito e. Angka keterlambatan penyerahan hasil pemeriksaan f. Angka kerusakan sampel darah g. Angka kesalahan pengambilan sampel h. Angka kesalahan pasien i. Pelaporan nilai kritis laboratorium 3. Pelayanan Radiologi dan Diagnostic Imagin a. Waktu Tunggu Hasil Pelayanan Thorax Foto b. Pelaksana Ekspertisi c. Kejadian Kegagalan Pelayanan Rontgen d. Waktu tunggu pemeriksaan Radiologi cito e. Angka pemeriksaan ulang f. Angka penolakan expertise g. Angka keterlambatan penyerahan hasil h. Angka kesalahan posisi pemeriksaan i. Angka reaksi obat kontras j. Penyampaian hasil radiologis kristis kepada dokter pengirim k. Respon time pem cito dari IGD l. Respon time USG cito dari IGD non obsgyn m. Respon time thorax konvensional 4. Prosedur Bedah a. Waktu tunggu operasi elektif b. Kejadian Kematian di meja operasi c. Tidak adanya kejadian operasi salah sisi d. Tidak adanya kejadian opersi salah orang e. Tidak adanya kejadian salah tindakan pada operasi f. Tidak adanya kejadian tertinggalnya benda asing/lain pada tubuh pasien setelah operasi g. Angka penundaan operasi h. Angka keterlambatan dimulainya operasi i. Angka infeksi luka/daerah operasi j. Angka ketidak lengkapan informed concent k. Angka ketidak lengkapan laporan operasi l. Angka ketidak lengkapan laporan anestesi 6 5. 6. 7. 8. m. Kepatuhan melaksanakan proses time out pada pasien pre operasi n. Ketidaksesuaian Diagnosis pra dan pasca bedah o. Marking Penggunaan Antibiotika dan Obat Lainnya a. Operasi bersih tanpa pemberian profilaxis antibiotik b. Penulisan resep sesuai formularium c. Penggunaan antibiotika di ICU sesuai dng hasil resistensi test d. Pemberian aspirin pada pasien AMI (IIL) e. Patients with ischemic stroke prescribed antithrombotic therapy at discharge (IIL) f. Patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter receiving anticoagulation therapy (IIL) g. Pediatric asthma patients who received systemic corticosteroids during hospitalization h. Patients who received VTE (Venous thrombo embolism) prophylaxis (or reasons of why this was not done) on the day of or day after hospital admission or surgery i. ICU patients who received VTE prophylaxis (or reasons of why this was not done) on the day of or day after hospital admission or surgery Kesalahan Medikasi (Medication Error) & KNC a. Ketepatan waktu pemberian antibiotika b. Ketepatan waktu pemberian injectie antibiotik pada pasien rawat inap. c. Kejadian Nyaris Cedera Peresepan Obat d. Kesalahan dan Kejadian Nyaris Cedera Medikasi, Pencegahan Adverse Drug Event Penggunaan Anestesi dan Sedasi a. Kelengkapan asesmen pre anestesia b. Pasien paska pembiusan di transfer dari recorvery room IBS ke ruang rawat inap sesuai dengan aldrette score c. Efek samping anestesi pada pasien SC d. Efek samping sedasi pada pasien endoscopy e. Komplikasi anastesi karena overdosis, f. Reaksi anastesi, g. Salah penempatan endotracheal tube. Penggunaan Darah dan Produk Darah a. Angka keterlambatan penyediaan darah untuk operasi elektif b. Angka kesalahan golongan darah c. Angka kesalahan jenis darah d. Angka reaksi transfusi darah e. Angka perbedaan hasil skrining f. Efektifitas penggunaan darah g. Kebutuhan darah bagi setiap pelayanan tranfusi h. Kejadian reaksi tranfusi 9. Ketersediaan, Isi dan Penggunaan RM Pasien; a. Kelengkapan pengisian rekam medik 24 jam setelah selesai pelayanan b. Kelengkapan Informed Concent setelah mendapatkan informasi yang jelas c. Waktu penyediaan dokumen rekam medik pelayanan rawat jalan d. Waktu penyediaan dokumen rekam medik pelayanan rawat inap 10. PPI, Surveilans dan Pelaporan a. Ada anggota Tim PPI yang terlatih b. Kegiatan pencatatan dan pelaporan infeksi nosokomial / HAI (Health Care Associated Infection) di RS (min 1 parameter) 11. Riset Klinis 7 Area manajerial 1. Pengadaan rutin alkes dan obat penting untuk memenuhi kebutuhan pasien; a. Ketersediaan obat dan alkes emergency di ruang resisutasi IGD b. Ketersedian obat di RS c. Ketersediaan obat kemoterapi di RS 2. Pelaporan aktivitas yang diwajibkan oleh peraturan perundang - undangan; a. Ketepatan waktu penyampaian keuangan sesuai Pedoman Akutansi RS (PARS) b. Ketepatan waktu laporan insiden keselamatan pasien c. Ketepatan waktu laporan dari unit kerja d. Ketepatan waktu laporan RS (RL) e. Kelengkapan laporan HIV f. Laporan KPRS paling lambat 2 x 14 jam 3. Manajemen risiko; a. Kejadian tertusuk limbah benda tajam infeksius b. Kejadian tertusuk jarum suntik c. Kejadian pasien pulang APS d. Dilakukan FMEA setahun sekali e. Pengadaan Barang beracun berbahaya (B-3) yang dilengkapi MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) 4. Manajemen penggunaan sumber daya; a. Utilisasi Ct-Scan b. Utilisasi ruang VIP c. Utilisasi USG Dopler 3 Dimensi d. Utilisasi C-ARM e. Utilisasi Ploroscopy f. Utilisasi peralatan kedokteran canggih 5. Harapan dan kepuasan pasien dan keluarga; a. Tingkat kepuasan pasien RJ, IGD, RI b. Survei kepuasan pasien menggunakan Index Kepuasan Masyarakat (IKM) c. Prosentasi pasien yang mengisi formulir angket pasien d. Survei kepuasaan pasien dalam satu bulan sekali 6. Harapan dan kepuasan staf; a. Tingkat kepuasan karyawan b. Tingkat kepuasan dokter c. Tingkat kepuasan perawat 7. Demografi pasien dan diagnosa klinis a. Laporan 10 besar penyakit (demografi pasien) b. Demografi pasien dengan diagnosis klinik DHF 8. Manajemen keuangan a. Cost recovery rate b. Current Ratio c. Return of invesment (ROI) 9. Pencegahan dan pengendalian dari kejadian yang dapat menimbulkan masalah bagi keselamatan pasein, keluarga pasien dan staf a. Edukasi hand hygiene b. Ketaatan cuci tangan penunjang c. Ketaatan penggunaan Alat Pelindung Diri (APD) 8 Sasaran Keselamatan Pasien 1. Ketepatan Identitas Pasien; a. Jumlah pasien tanpa gelang identitas b. Specimen tidak diberi label dengan 2 tanda pengenal 2. Peningkatan Komunikasi yang efektif a. Verbal order di tandatangani dokter dalam 24 jam b. hasil lab pertelp di read back 3. Peningkatan keamanan obat yang perlu di waspadai a. % high alert medication yang masih ditemukan di unit perawatan b. % high alert medication yang ditemukan tanpa label alert 4. Kepastian tepat lokasi, tepat prosedur, tepat pasien operasi a. Time out dilaksanakan dengan lengkap sebelum operasi b. Penandaan lokasi operasi ( side marker ) 5. Pengurangan infeksi terkait pelayanan kesehatan a. Angka kepatuhan hand hygiene 6. Pengurangan resiko jatuh a. Jumlah pasien jatuh b. pelaksanaan asesmen resiko di instalasi rawat inap Joint Commission International Library of Measures 1. Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) a. Aspirin at Arrival Aspirin received within 24 hours of arrival to the hospital for patients having an acute myocardial infarction (AMI). b. Aspirin Prescribed at Discharge Aspirin prescribed at discharge for patients who had an acute myocardial infarction. c. ACEI or ARB for LVSD ACEI (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor) or ARB (angiotensin receptor blocker) for patients who have LVSD (Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction) after having an acute myocardial infarction. d. Adult Smoking Cessation Advice/Counseling Adult smoking cessation advice/counseling given to patients who had an acute myocardial infarction. e. Beta-blocker prescribed at discharge Beta-blocker prescribed at discharge for patients who had an acute myocardial Infarction f. Inpatient Mortality Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients who expire during the hospital stay 2. Heart Failure (HF) a. Evaluation of LVS Function Heart failure patients with documentation in the hospital record that left ventricular systolic (LVS) function was evaluated before arrival; during hospitalization, or is planned for after discharge b. ACEI or ARB for LVSD ACEI (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor) or ARB (angiotensin receptor blocker) for heart failure patients who have LVSD (Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction) 9 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. c. Adult Smoking Cessation Advice/Counseling Adult smoking(cigarettes) cessation advice/counseling given to heart failure patients Stroke (STK) a. Discharged on Antithrombotic Therapy Ischemic stroke patients prescribed antithrombotic therapy at hospital discharge b. Anticoagulation Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter Ischemic stroke patients with atrial fibrillation/flutter who are prescribed anticoagulation therapy at hospital discharge c. Stroke Education Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients or their caregivers who were given educational material addressing ALL of the following: Activation of emergency medical system (if available in region), need for followup after discharge, medications prescribed at discharge, risk factors for stroke, and warning signs and symptoms of stroke. d. Assessed for Rehabilitation Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients who were assessed for or received rehabilitation services. Children’s Asthma Care (CAC) a. Relievers for Inpatient Asthma Use of relievers in pediatric patients admitted for inpatient treatment of asthma b. Systemic Corticosteroids for Inpatient Asthma Use of systemic corticosteroids in pediatric patients admitted for impatient treatment of asthma Hospital-Based Inpatient Psychiatric Service (HBIPS) a. Hours of physical restraint use The total number of hours that all patients admitted to a hospitalbased inpatient psychiatric setting were maintained in physical restraint b. Hours of seclusion use The total number of hours that all patients admitted to a hospitalbased inpatient psychiatric setting were held in seclusion. Nursing-Sensitive Care (NSC) a. Pressure Ulcer Prevalence (HospitalAcquired) Patients that have hospital-acquired (nosocomial) category/stage II or greater pressure ulcer(s) on the day of the prevalence study b. Patient Falls All documented falls with or without injury, experienced by patients in a calendar month. c. Falls with Injury All documented falls by a patient with an injury level of “minor” (2) or greater. Perinatal Care (PC) a. Elective Delivery Patients with elective vaginal deliveries or elective cesarean sections at >= 37 and < 39 weeks of gestation completed b. Cesarean Section Nulliparous women with a term, singleton baby in a vertex position delivered by cesarean section 10 c. Exclusive Breast Feeding Exclusive breast milk feeding during the newborn's entire hospitalization 8. Pneumonia (PN) a. Pneumococcal Vaccination Pneumonia patients, aged 65 and older, who were screened for pneumococcal vaccine status and were administered the vaccine prior to discharge, if indicated b. Adult Smoking Cessation Advice/Counseling Adult smoking cessation advice/counseling given to patients who smoke cigarettes and who are hospitalized for pneumonia c. Influenza Vaccination Pneumonia patients, aged 50 and older, who during the flu season, were screened for influenza vaccine status and were vaccinated prior to discharge, if indicated 9. Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) a. Prophylactic Antibiotic Received Within One Hour Prior to Surgical Incision Hip Arthroplasty Surgical patients with prophylactic antibiotics initiated within one hour prior to surgical incision. Patients who received Vancomycin or a Fluroquinolone for prophylactic antibiotics should have the antibiotics initiated within two hours prior to surgical incision. Due to the longer infusion time required for Vancomycin and Fluroquinolone, it is acceptable to start these antibiotics within two hours prior to incision time b. Prophylactic Antibiotic Received Within One Hour Prior to Surgical Incision-Knee Arthroplasty Surgical patients with prophylactic antibiotics initiated within one hour prior to surgical incision. Patients who received Vancomycin or a Flurooquinolone for prophylactic antibiotics should have the antibiotics initiated within two hours prior to surgical incision. Due to the longer infusion time required for Vancomycin and Fluroquinolone, it is acceptable to start these antibiotics within two hours prior to incision time. c. Prophylactic Antibiotic Selection for Surgical Patients-Hip Arthroplasty Surgical patients who received prophylactic antibiotics consistent with current Hip Arthroplasty guidelines, Appendix C, Table 3.2, Prophylactic Antibiotic Regimen Selection for Surgery d. Prophylactic Antibiotic Selection for Surgical Patients-Knee Arthroplasty Surgical patients who received prophylactic antibiotics consistent with current Knee Arthroplasty guidelines Appendix C, Table 3.2, Prophylactic Antibiotic Regimen Selection for Surgery e. Prophylactic Antibiotics Discontinued Within 24 Hours After Surgery End Time- Hip Arthroplasty Surgical patients, who had a Hip Arthroplasty, whose prophylactic antibiotics were discontinued within 24 hours after Anesthesia End Time f. Prophylactic Antibiotics Discontinued Within 24 Hours After Surgery End Time Knee Arthroplasty 11 Surgical patients, who had a Knee Arthroplasty, whose prophylactic antibiotics were discontinued within 24 hours after Anesthesia End Time g. Surgery Patients with Recommended Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Ordered Surgery patients with recommended Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis ordered anytime from hospital arrival to 24 hours after Anesthesia End Time, h. Surgery Patients Who Received Appropriate Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Within 24 hours Prior to Surgery to 24 Hours After Surgery Surgery patients who received appropriate Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis within 24 hours prior to Anesthesia Start Time to 24 hours after Anesthesia End Time 10. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) a. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis This measure assesses the number of patients who received VTE prophylaxis or have documentation why no VTE prophylaxis was given the day of or the day after hospital admission or surgery end date for surgeries that start the day of or the day after hospital admission. b. Intensive Care Unit Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis This measure assesses the number of patients who received VTE prophylaxis or have documentation why no VTE prophylaxis was given the day of or the day after the initial admission (or transfer) to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) or surgery end date for surgeries that start the day of or the day after ICU admission (or transfer). 12 NOTULEN RAPAT PEMILIHAN PRIORITAS PROGRAM PMKP 13 PEMERINTAH KABUPATEN KARAWANG BADAN LAYANAN UMUM DAERAH RUMAH SAKIT UMUM DAERAH KELAS B NON PENDIDIKAN JL. Galuh Mas Raya No. 1 Sukaharja Telukjambe Timur Telp (0267) 640444, 640555 Fax (0267) 640666 KARAWANG Notulen Rapat Pemilihan Prioritas Program Peningkatan Mutu dan Keselamatan Pasien (PMKP) Hari : Sabtu Tanggal : 12 Maret 2016 Jam : 09.00 – 12.00 Tempat : Swiss Bellin Hotel Karawang Peserta yang diundang : 133 Orang Peserta yang hadir : 80 Orang (60,15%) Materi Pembahasan : Pemilihan Prioritas Program PMKP 1. Menetapkan Indikator kunci/prioritas di 10 area klinik 2. Menetapkan 5 Indikator klinis sesuai Joint Commission International Library 3. Menetapkan Indikator kunci/prioritas di 9 area manajemen 4. Menetapkan Indikator kunci/prioritas di sasaran keselamatan pasien (SKP) Pembahasan : 1. 10 Indikator Kunci/Prioritas Area Klinik No Area Klinis Indikator 1 Asesmen Pasien Asesmen medis pasien bedah 2 Pelayanan Laboratorium 3 Pelayanan Radiologi dan Diagnostic Imagin Prosedur Bedah 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Penggunaan Antibiotika Dan Obat Lainnya Kesalahan Medikasi (Medication Error) & KNC Penggunaan Anestesi Dan Sedasi Penggunaan Darah Dan Produk Darah Ketersediaan, Isi Dan Penggunaan RM Pasien; PPI, Surveilans Dan Pelaporan Standar 100% sebelum operasi Waktu tunggu hasil pelayanan ≤ 140 menit Kimia laboratorium darah & drh rutin Kejadian Kegagalan Kerusakan Foto ≤ Pelayanan Rontgen 2% Angka ketidak lengkapan 0% informed concent Penulisan resep sesuai 100% formularium Kejadian Nyaris Cedera 0% Peresepan Obat Salah penempatan endotracheal tube. Angka kesalahan jenis darah 10% 0% Kelengkapan Informed 100% Concent setelah mendapatkan informasi yang jelas Ada anggota Tim PPI yang Anggota Tim PPI terlatih yang terlatih 75 % 14 2. 5 Indikator Klinis Joint Commission International Library International Library of No MeasuresMeasure Sets 1 Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) Measure Short Name Aspirin at Arrival 2 Stroke (STK) Stroke Education 3 Children’s Systemic Asthma Care Corticosteroids for (CAC) Inpatient Asthma 4 Perinatal Care Exclusive (PC) Feeding 5 Pneumonia (PN) Breast Adult Smoking Cessation Advice/Counseling Measure Description Standar Aspirin received within 24 hours of arrival to the hospital for patients having an acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke patients or their caregivers who were given educational material addressing ALL of the following: Activation of emergency medical system (if available in region), need for follow-up after discharge, medications prescribed at discharge, Use of systemic corticosteroids in pediatric patients admitted for impatient treatment of asthma Exclusive breast milk feeding during the newborn's entire hospitalization Adult smoking cessation advice/counseling given to patients who smoke cigarettes and who are hospitalized for pneumonia 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 3. 9 Indikator Kunci/Prioritas Area Manajemen No Area Manajerial 1 Pengadaan rutin alkes dan obat penting untuk memenuhi kebutuhan pasien; 2 Pelaporan aktivitas yang diwajibkan oleh peraturan perundang - undangan; 3 Manajemen risiko; Indikator Ketersediaan obat dan alkes emergency di ruang resisutasi IGD Standar 100% Ketepatan waktu penyampaian laporan keuangan sesuai Pedoman Akutansi RS (PARS) Dilakukan FMEA setahun sekali Sebelum Tgl 7 setiap bulan 100% 15 4 5 6 7 8 9 Manajemen penggunaan Utilisasi Ct-Scan sumber daya; Harapan dan kepuasan Survei kepuasan pasien pasien dan keluarga; menggunakan Index Kepuasan Masyarakat (IKM) Harapan dan kepuasan Tingkat kepuasan karyawan staf; Demografi pasien dan Demografi pasien dengan diagnosa klinis diagnosis klinik DHF Manajemen keuangan Cost recovery rate Pencegahan dan Edukasi hand hygiene pengendalian dari kejadian yang dapat menimbulkan masalah bagi keselamatan pasien, keluarga pasien dan staf 100% 2 kali / Tahun 70% 100% 80% 100% 4. 6 Indikator Kunci/Prioritas Sasaran Keselamatan Pasien (SKP) No 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sasaran Keselamatan Pasien Ketepatan Identitas Pasien; Peningkatan Komunikasi yang efektif Peningkatan keamanan obat yang perlu di waspadai Kepastian tepat lokasi, tepat prosedur, tepat pasien operasi Pengurangan infeksi terkait pelayanan kesehatan Pengurangan resiko jatuh Indikator Standar Jumlah pasien tanpa gelang identitas hasil laboratorium per telpon di read back % high alert medication yang ditemukan tanpa label alert Time out dilaksanakan dengan lengkap sebelum operasi Angka kepatuhan hand hygiene pelaksanaan asesmen resiko di instalasi rawat inap 0% 100% 0% 100% 100% 100% 16 Penetapan Pelayanan Prioritas NO 1 2 3 4 5 PELAYANAN PRIORITAS Aspirin at Arrival Stroke Education Systemic Corticosteroids for Inpatient Asthma Exclusive Breast Feeding Adult Smoking Cessation Advice/Counseling HIGH RISK (Nilai x Bobot = Skor) Rentang Nilai = 1 - 5 Bobot = 50 N B S 5 50 250 HIGH VOLUME (Nilai x Bobot = Skor) Rentang Nilai = 1 - 5 Bobot = 30 N B S 5 30 150 HIGH COST (Nilai x Bobot = Skor) Rentang Nilai = 1 - 5 Bobot = 20 N B S 2 20 40 JUMLAH 440 3 50 150 5 30 150 2 20 40 340 5 50 250 5 30 150 3 20 60 460 1 50 50 5 30 150 1 20 20 220 1 50 50 5 30 150 1 20 20 220 Keterangan: Pelayanan prioritas perbaikan : Children’s Asthma Care (CAC), Penggunaan kortikosteroid sistemik pada pengobatan asthma bagi pasien-pasien anak yang menjalani rawat inap (Use of systemic corticosteroids in pediatric patients admitted for impatient treatment of asthma) 17 Penetapan Area Prioritas HIGH RISK HIGH VOLUME HIGH COST (Nilai x Bobot = Skor) (Nilai x Bobot = Skor) (Nilai x Bobot = Skor) Rentang Nilai = 1 - 5 Rentang Nilai = 1 - 5 Rentang Nilai = 1 - 5 Bobot = 50 Bobot = 30 Bobot = 20 AREA NO JUMLAH PRIORITAS 1 2 3 4 5 ICU IGD IBS Rawat Inap Farmasi N B S N B S N B S 4 50 200 3 30 4 20 80 370 5 50 250 3 30 3 20 60 400 3 50 250 3 30 90 90 90 3 20 60 300 3 50 150 5 30 150 3 20 60 360 4 50 200 5 30 150 3 20 60 350 Keterangan: Pelayanan Area Prioritas : Instalasi Gawat Darurat (IGD) 18 Kriteria Pemilihan Indikator Utama Score No Definisi 1 Min 1 2 3 High Risk ( Indikator yang dipilih merupakan kondisi berresiko pada pasien) High Volume ( Indikator yang dipilih merupakan yang sering terjadi) High Cost ( Indikator yang dipilih merupakan kondisi yang menimbulkan kerugian keuangan) 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 Max 5 5 5 Tidak Timbul Resiko Timbul Resiko Kecil Timbul Resiko Sedang Timbul Resiko Besar Timbul Resiko Sangat Besar Sangat Jarang (> 5 Thn) Jarang (2-5 Thn/kali) Dpt terjadi dlm 1-2 thn (beberapa kali/thn) Sering sekali (terjadidlm minggu/bulan) Tidak timbul kerugian keuangan Timbul kerugian keuangan kecil Timbul kerugian keuangan sedang Timbul kerugian keuangan besar Timbul kerugian keuangan sangat besar 19 Kesimpulan : 10 Indikator kunci/prioritas di area klinik 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Asesmen medis pasien bedah sebelum operasi Waktu tunggu hasil pelayanan laboratorium Kejadian Kegagalan Pelayanan Rontgen Angka ketidak lengkapan informed concent Penulisan resep sesuai formularium Kejadian Nyaris Cedera Peresepan Obat Salah penempatan endotracheal tube. Angka kesalahan jenis darah Kelengkapan Informed Concent setelah mendapatkan informasi yang jelas Ada anggota Tim PPI yang terlatih 5 Indikator Klinis Joint Commission International Library 1 2 3 4 5 Aspirin at Arrival Stroke Education Systemic Corticosteroids for Inpatient Asthma Exclusive Breast Feeding Adult Smoking Cessation Advice/Counseling 9 Indikator Kunci/Prioritas Area Manajemen 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Ketersediaan obat dan alkes emergency di ruang resisutasi IGD Ketepatan waktu penyampaian keuangan sesuai Pedoman Akutansi RS (PARS) Dilakukan FMEA setahun sekali Utilisasi Ct-Scan Survei kepuasan pasien menggunakan Index Kepuasan Masyarakat (IKM) Tingkat kepuasan karyawan Demografi pasien dengan diagnosis klinik DHF Cost recovery rate Edukasi hand hygiene 6 Indikator Kunci/Prioritas Sasaran Keselamatan Pasien (SKP) 1 2 3 4 5 6 Jumlah pasien tanpa gelang identitas hasil laboratorium per telpon di read back % high alert medication yang ditemukan tanpa label alert Time out dilaksanakan dengan lengkap sebelum operasi Angka kepatuhan hand hygiene pelaksanaan asesmen resiko di instalasi rawat inap 20 Pelayanan prioritas perbaikan : Children’s Asthma Care (CAC), Penggunaan kortikosteroid sistemik pada pengobatan asthma bagi pasien-pasien anak yang menjalani rawat inap (Use of systemic corticosteroids in pediatric patients admitted for impatient treatment of asthma) Pelayanan Area Prioritas : Instalasi Gawat Darurat (IGD) Pemimpin Rapat 21 LAMPIRAN 22 UNDANGAN 23 DAFTAR HADIR 24 PEMERINTAH KABUPATEN KARAWANG BADAN LAYANAN UMUM DAERAH RUMAH SAKIT UMUM DAERAH KELAS B NON PENDIDIKAN JL. Galuh Mas Raya No. 1 Sukaharja Telukjambe Timur Telp (0267) 640444, 640555 Fax (0267) 640666 KARAWANG Susunan Acara PEMILIHAN PRIORITAS PROGRAM PENINGKATAN MUTU DAN KESELAMATAN PASIEN (PMKP) RSUD KARAWANG Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang Waktu Acara PIC 09.00 - 09.05 09.06 – 09.25 09.26 – 11.45 Pembukaan............................................................ Sambutan Direktur RSUD Karawang .................... Rapat Pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP ................................................................... Penutup/Do`a ........................................................ Eva Puspa W, SKM, MM dr. H. Asep Hidayat Lukman, MM 11.46 – 11.50 dr Irwin, Sp.PD H. Deden Mustofa Kamil, SKM 25 DOKUMENTASI GAMBAR 26 Rapat pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 di Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang dibuka oleh Direktur RSUD Karawang dr. H. Asep Hidayat Lukman, MM Peserta yang menghadiri rapat pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 di Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang sebanyak 80 orang. 27 Salah satu sudut peserta yang hadir saat rapat pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 di Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang dari kiri, Heru Pamuji, Amd.PK (Rekam Medis), Dadang Sukardi, Amd.PK (Rekam Medis), Ahmad Rofiudin, Amd.PK (Rekam Medis), Kurniasih, S.Kep (Bidang Keperawatan), Ani Muthia, SKM, MARS (Bidang Perencanaan) 28 Direktur RSUD Karawang, dr. H. Asep Hidayat Lukman, MM didampingi dr. Irwin, Sp.PD Ketua Pokja PMKP saat pembukaan rapat pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 di Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang. dr. Irwin, Sp.PD Ketua Pokja PMKP saat presentasi rapat pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 di Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang 29 dr. Ade Nurkacan, Sp.AN dan dr. Irwin, Sp.PD Ketua Pokja PMKP saat berdiskusi pada rapat pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 di Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang Pose bersama saat setelah acara rapat pembahasan pemilihan prioritas program PMKP Sabtu, 12 Maret 2016 di Swiss Bellinn Hotel Karawang. Dari kiri dr. Endang Elisawaty, Sp.S, dr Achmad Rizky Herda, Sp.U, dr. Irwin, Sp.PD, dr. Irwan, dr. H. Asep Hidayat Lukman, MM (Direktur RSUD Karawang), dr. Ade Nurkacan, Sp.AN, Sutarman, S.Kep, Sri Endah, S.Kep, Ners (belakang) dan dr. David A, Sp.OG. 30