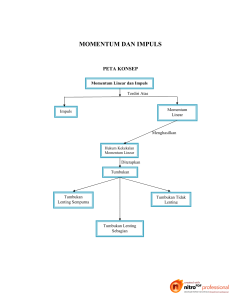
IMPULS DAN MOMENTUM Mata Kuliah : FISIKA DASAR 1 Nama Dosen www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Apa itu Momentum? Momentum benda adalah perkalian antara massa benda dan kecepatannya. MOMENTUM p mv Momentum adalah besaran vektor, sehingga penting untuk memperhatikan arah momentumnya www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Apa itu Impuls? Impuls adalah gaya yang bekerja pada durasi waktu yang pendek. IMPULS I F t Untuk gaya yang bergantung waktu, impuls dan momentum lebih berguna untuk menyelesaikan persoalan daripada hukum ke-2 Newton www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Bagaimana Impuls dan Momentum saling berhubungan Cara kerja momentum sama dengan cara kerja energi. Momentum sistem akan berubah jika diberi impuls. I x px www.its.ac.id pix I x p fx INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Apakah momentum kekal? Momentum total sistem terisolasi bersifat kekal (conserved). Partikel dari sistem terisolasi hanya berinteraksi antar partikel, tidak dengan lingkungan. Bagaimanapun interaksi antar partikelnya, momentum awal = momentum akhir www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Bagaimana momentum diterapkan pada tumbukan? Penerapan hukum kekekalan momentum adalah pada kasus tumbukan. 1. Tumbukan tidak lenting sama sekali. momentum kekal, energi tidak kekal 2. Tumbukan lenting sempurna. baik momentum maupun energi kekal www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Dimana momentum diterapkan? Dua aplikasi penting dari hukum kekekalan momentum • Ledakan (explosion). Interaksi singkat yang memisahkan dua atau lebih dari sebuah objek • Pelepasan roket (rocket propulsion). Meningkatnya kecepatan roket karena memisahkan sebagian dari massa. www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Tumbukan • Tumbukan. Interaksi antar dua objek dalam tempo yang singkat. • Tumbukan antar bola tenis dan raket berlangsung cepat, namun tidak instan Terjadi deformasi struktur pada bola tenis sebelum berbalik arah www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Impuls selama tumbukan • Gaya yang besar terjadi dalam tempo yang singkat. Dinamakan gaya impulsive Mula-mula partikel (bola tenis) bergerak ke arah kiri 𝑣𝑖𝑥 , kemudian dikenai gaya impulsive 𝐹𝑥 (𝑡) ke kanan, dan akhirnya berbalik bergerak ke kanan 𝑣𝑓𝑥 www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Momentum • Momentum adalah vector, dengan satuan kg.m/s • Vektor momentum partikel dapat dijabarkan pada arah sumbu x dan sumbu y www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Impuls • Hukum Newton II dapat diformulasikan sebagai turunan momentum terhadap waktu • Diintegralkan terhadap waktu , sehingga • Didefinisikan impuls sebagai www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Prinsip Momentum • Partikel mengalami gaya impulsif pada arah x • Impuls membuat partikel mengalami perubahan momentum I x px www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Analogi dengan prinsip energi • Ketika sebuah objek dikenai gaya, maka gaya itu menghasilkan kerja pada objek dan menciptakan impuls pada objek www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Kekekalan momentum • Dua objek saling bertumbukan seperti gambar • Abaikan semua gaya eksternal pada objek • Karena hanya ada gaya antar objek, maka penjumlahan momentumnya • Berlaku kekekalan momentum • Jumlah momentum sebelum dan sesudah sama www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Contoh hukum kekekalan momentum Sebuah kereta bergerak dengan kecepatan 𝑣𝑖 ke kanan. Menumbuk kereta yang diam. Kereta kemudian bergerak bersama-sama. Tentukan kecepatan akhir kedua kereta? Berdasarkan hokum kekekalan momentum m1 (vfx)1 + m2 (vfx)2 = m1 (vix)1 + m2 (vix)2 mvf + mvf = 2mvf = mvi + 0 Suku massa dapat dicoret, sehingga diperoleh 𝑣𝑓 = 𝑣𝑖 /2 www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Sistem Partikel • Semisal terdapat N partikel saling berinteraksi • Pada gambar, N = 3 • Sistem memiliki momentum total • Aplikasikan hukum Newton II pada tiap partikel, diperoleh rerata perubahan momentum total pada sistem www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Momentum sistem • Gaya interaksi berpasang-pasangan (aksi-reaksi) • Konsekuensinya, total gaya interaksi = 0, sehingga • Rerata perubahan momentum total dari sistem sama dengan gaya total yang bekerja pada system • Gaya internal tidak mempengaruhi www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Hukum kekekalan momentum • Untuk sistem yang terisolasi, • Momentum total gas + roket kekal, sehingga roket mengalami percepatan ke atas, sebagaimana gas mengalami percepatan ke bawah www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Hukum kekekalan momentum Sistem terisolasi = system yang gaya totalnya sama dengan nol atau Dengan kata lain www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Hukum kekekalan bergantung pilihan kerangka acuan • Bola dijatuhkan ke Bumi • Bola sebagai kerangka acuan • Gaya gravitasi sebagai gaya eksternal • Momentum system tidak kekal (not conserved) www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Hukum kekekalan bergantung pilihan kerangka acuan • Bola jatuh dan menuju Bumi • Definisikan bola dan bumi sebagai satu system • Gaya gravitasi sebagai interaksi di dalam system • Sistem terisolasi sehingga berlaku kekekalan momentum www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Tumbukan tidak lenting • Tumbukan antar dua objek yang kemudian kedua partikel saling rekat satu dengan yang lain disebut tumbukan tidak lenting sama sekali Contoh : 1. Permen karet yang jatuh dan menempel dilantai 2. Dart menumbuk papan dart www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Tumbukan elastik • Tumbukan antar dua objek yang energy mekanik total tidak berkurang • Disebut sebagai tumbukan lenting sempurna Contohnya : Tumbukan antar dua objek yang keras seperti bola biliar, bola besi, dan yang lainnya www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Tumbukan lenting sempurna • Partikel 1 bermassa 𝑚1 bergerak dengan kecepatan (𝑣𝑖𝑥 )1 ke kanan menumbuk secara lenting sempurna partikel 2 bermassa 𝑚2 yang diam • Kecepatan bola setelah tumbukan adalah (𝑣𝑓𝑥 )1 dan (𝑣𝑖𝑥 )2 • Momentum kekal saat tumbukan terisolasi • Energi kinetik partikel kekal selama tumbukan www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Ledakan • Ledakan (explosion) adalah kebalikan dari tumbukan • Pertama, partikel memiliki interaksi internal singkat, yang kemudian saling menjauh satu sama lain • Jika system terisolasi selama ledakan, maka momentum kekal www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Pelepasan Roket dan Jet • Jika dipandang roket dan gas sebagai satu sistem, proses pembakaran dan ekspulsion dianggap sebagai gaya internal • Nilai momentum = 0 • Roket melaju ke atas, gas melaju ke bawah www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia LATIHAN SOAL Momentum is A. Mass times velocity. B. ½ mass times speed-squared. C. The area under the force curve in a force-versus-time graph. D. Velocity per unit mass. www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Impulse is A. A force that is applied at a random time. B. A force that is applied very suddenly. C. The area under the force curve in a force-versus-time graph. D. The time interval that a force lasts. www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A method for “momentum accounting,” introduced in this chapter, is A. B. C. D. E. www.its.ac.id Credit-debit tables. Impulse-versus-time graphs. Momentum bar charts. Momentum conservation pools. Momentum spreadsheets. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia The total momentum of a system is conserved A. B. C. D. www.its.ac.id Always. If the system is isolated. If the forces are conservative. Never; it’s just an approximation. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia In an inelastic collision, A. B. C. D. E. www.its.ac.id Impulse is conserved. Momentum is conserved. Force is conserved. Energy is conserved. Elasticity is conserved. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A perfectly elastic collision is a collision A. Between two springs. B. That conserves thermal energy. C. That conserves kinetic energy. D. That conserves potential energy. E. That conserves mechanical energy. www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia The cart’s change of momentum Δpx is A. B. C. D. E. www.its.ac.id –20 kg m/s –10 kg m/s 0 kg m/s 10 kg m/s 30 kg m/s INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A 2.0 kg object moving to the right with speed 0.50 m/s experiences the force shown. What are the object’s speed and direction after the force ends? A. 0.50 m/s left B. At rest C. 0.50 m/s right D. 1.0 m/s right E. 2.0 m/s right www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A 2.0 kg object moving to the right with speed 0.50 m/s experiences the force shown. What are the object’s speed and direction after the force ends? A. 0.50 m/s left B. At rest C. 0.50 m/s right D. 1.0 m/s right E. 2.0 m/s right www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A light plastic cart and a heavy steel cart are both pushed with the same force for 1.0 s, starting from rest. After the force is removed, the momentum of the light plastic cart is that of the heavy steel cart. A. greater than B. equal to C. less than D. Can’t say. It depends on how big the force is. www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia Two 1.0 kg stationary cue balls are struck by cue sticks. The cues exert the forces shown. Which ball has the greater final speed? A. B. C. www.its.ac.id Ball 1 Ball 2 Both balls have the same final speed. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia You awake in the night to find that your living room is on fire. Your one chance to save yourself is to throw something that will hit the back of your bedroom door and close it, giving you a few seconds to escape out the window. You happen to have both a sticky ball of clay and a super-bouncy Superball next to your bed, both the same size and same mass. You’ve only time to throw one. Which will it be? Your life depends on making the right choice! www.its.ac.id A. Throw the Superball. B. Throw the ball of clay. C. It doesn’t matter. Throw either. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A mosquito and a truck have a head-on collision. Splat! Which has a larger change of momentum? A. The mosquito B. The truck C. They have the same change of momentum. D. Can’t say without knowing their initial velocities. www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia The 1 kg box is sliding along a frictionless surface. It collides with and sticks to the 2 kg box. Afterward, the speed of the two boxes is www.its.ac.id A. 0 m/s B. 1 m/s C. 2 m/s D. 3 m/s E. There’s not enough information to tell. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia The two boxes are sliding along a frictionless surface. They collide and stick together. Afterward, the velocity of the two boxes is www.its.ac.id A. 2 m/s to the left. B. 1 m/s to the left. C. 0 m/s, at rest. D. 1 m/s to the right. E. 2 m/s to the right. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A 200 g ball moves to the right at 2.0 m/s. It has a head-on, perfectly elastic collision with a 100 g ball that is moving toward it at 3.0 m/s. What are the final velocities of both balls? www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia The two boxes are on a frictionless surface. They had been sitting together at rest, but an explosion between them has just pushed them apart. How fast is the 2 kg box going? www.its.ac.id A. 1 m/s B. 2 m/s C. 4 m/s D. 8 m/s E. There’s not enough information to tell. INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia A cart is rolling at 5 m/s. A heavy lead weight is suspended by a thread beneath the cart. Suddenly the thread breaks and the weight falls. Immediately afterward, the speed of the cart is A. Less than 5 m/s B. Still 5 m/s C. More than 5 m/s www.its.ac.id INSTITUT TEKNOLOGI SEPULUH NOPEMBER, Surabaya - Indonesia






![[SmartArtPro]_Sample Free](http://s1.studylibid.com/store/data/000406698_1-dcd605c39d6512b7b70072b8c19d3987-300x300.png)