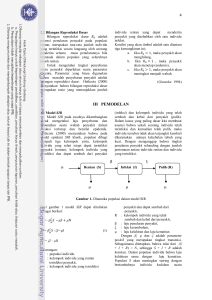
Analisis kestabilan model sir, sir vaksinasi, seir dan
advertisement

ABSTRACT ACE SUHENDAR. Stability analysis of mathematical models: SIR , SIR with vaccination, SEIR and MSEIR of the outbreak of measles diseases. Supervised by ALI KUSNANTO and PAIAN SIANTURI. Measles disease is an extremely dangerous disease. It caused by virus that spreads through direct to the contact with victims or air. Measles disease can cause complication, mustle disfunction and organ, physical defect, paralysis and death. A vaccination program is a powerful method to control the measles disease outbreak. The measles disease outbreak can be studied using mathematical model. The model is known as SIR, SIR of vaccination, SEIR and MSEIR epidemic model. In this research, the SIR of epidemic model, SIR of vaccination, SEIR and MSEIR is derived by including the factors of birth, death, vaccination, body profection and immunity. The vaccination is held to prevent the measles disease outbreak. Based on stability analysis conducted, the SIR model, SIR of vaccination, SEIR and MSEIR produced two equilibrium points, i.e, disease free and endemic equilibrium. The analysis conducted were also considering the basic reproduction rate and the minimum level of vaccination. If the vaccination level less than the minimum level, than the measles disease becomes endemic and for the vaccination level more than the minimum level, than the disease dies out. If , then the disease free equilibrium point is a stable node and the endemic equilibrium point is an unstable spiral, meaning that virus can be removed from the population. If , then the disease free equilibrium point is a saddle and the endemic equilibrium point is a stable spiral, meaning that virus remained. Also, the in the MSEIR model was found to be smaller than in the other models. This indicates that the MSEIR model was faster to reach the stabile level. ABSTRAK ACE SUHENDAR. Analisis Kestabilan Model SIR, SIR vaksinasi, SEIR dan MSEIR Sebagai Model-model Penyebaran Penyakit Campak (Measles). Dibimbing oleh ALI KUSNANTO dan PAIAN SIANTURI. Penyakit campak (measles) merupakan penyakit yang sangat berbahaya, penyakit ini disebabkan oleh virus yang dapat menyebar melalui kontak langsung dengan penderita dan udara. Penyakit campak (measles) dapat menyebabkan komplikasi, kerusakan otak dan organ tubuh yang lainnya, cacat seumur hidup, kelumpuhan dan bahkan kematian. Program vaksinasi merupakan metode yang baik untuk mencegah penyebarannya. Penyebaran penyakit ini dapat dipelajari dengan mengunakan model matematika. Model tersebut dikenal sebagai model endemik SIR, SIR vaksinasi, SEIR dan MSEIR. Pada penelitian ini, model SIR, SIR vaksinasi, SEIR dan MSEIR diturunkan ulang dengan memperhatikan faktor kelahiran, kematian, vaksinasi dan kekebalan tubuh. Analisis kestabilan terhadap model SIR, SIR vaksinasi, SEIR dan MSEIR ini menghasilkan dua titik tetap yaitu titik tetap tanpa penyakit dan titik tetap endemik. Analisis yang dilakukan menghasilkan bilangan reproduksi dasar dan tingkat vaksinasi minimum yang dibutuhkan agar berhasil dalam mencegah penyebaran penyakit campak (measles). Untuk nilai tingkat vaksinasi di bawah tingkat vaksinasi minimum, penyakit akan bersifat endemik dan untuk nilai vaksinasi di atas nilai tingkat vaksinasi minimum, penyakit akan menghilang dari populasi individu. Ketika titik tetap tanpa penyakit bersifat simpul stabil, dan titik tetap endemik bersifat spiral takstabil sehingga virus akan hilang dari populasi. Ketika titik tetap tanpa penyakit bersifat sadel, dan titik tetap endemik akan bersifat spiral stabil sehingga virus akan bertahan dalam populasi. Dari ke empat model tersebut diperoleh bahwa bilangan reproduksi dasar pada model MSEIR lebih kecil daripada model SIR, SIR vaksinasi dan SEIR, hal ini menunjukkan bahwa model MSEIR akan lebih cepat mencapai kondisi stabil.