Tugas Biofungsi-Saraf
advertisement
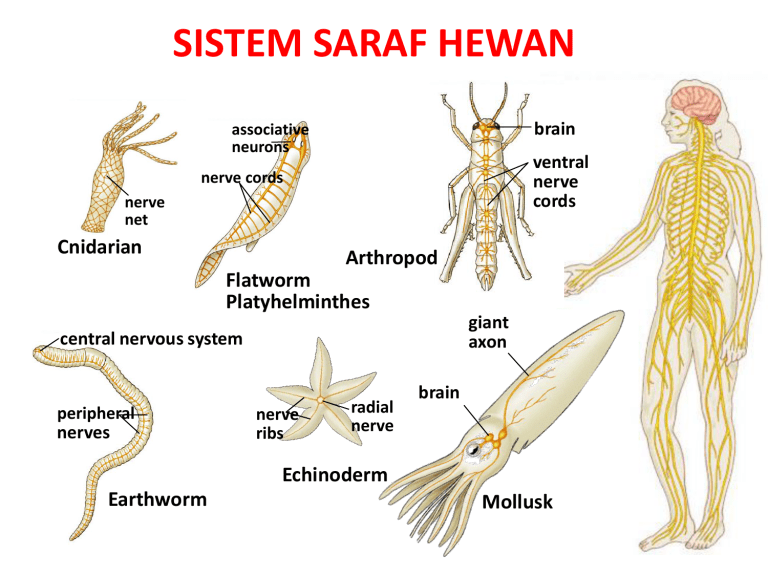
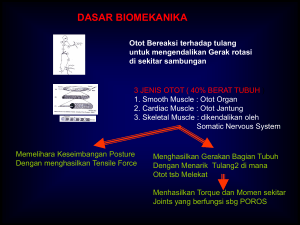
SISTEM SARAF HEWAN brain associative neurons ventral nerve cords nerve cords nerve net Cnidarian Arthropod Flatworm Platyhelminthes giant axon central nervous system peripheral nerves nerve ribs radial nerve brain Echinoderm Earthworm Mollusk Cefalisasi = Evolusi Otak Cephalization = clustering of neurons in “brain” at front (anterior) end of bilaterally symmetrical animals where sense organs are Kumpulan Neuron Saraf korda Saraf rusuk Saraf radial Saraf jalat Cnidarian Simplest nervous system no control of complex actions Echinodermata More organization but still based on nerve nets; supports more complex movement Cacing Pipih Platyhelminthes Simplest, defined central nervous system more complex muscle control Cefalisasi = Evolusi Otak Interneuron bertambah banyak di dalam Otak Sistem Saraf Pusat Akson Raksasa Sistem Saraf Tepi Cacing Tanah Otak Otak ventral nerve cords Molluska Arthropoda More complex brains connected to all other parts of body by peripheral nerves More complex brains in predators most sophisticated invertebrate nervous system Further brain development ganglia = neuron clusters along CNS Evolusi Otak Vertebrata Otak Depan Otak Depan Serebrum Dominan Shark Otak Belakang Frog Crocodile Cat Human Spinal cord Hind: Medulla oblongata Hind: Serebellum Optic tectum Midbrain Fore: Serebrum Organ Olfaktori Otak Depan Bird Perkembangan Otak Manusia Otak Manusia Pembagian Fungsional Otak • Otak Belakang (Hind Brain) Mengendalikan Fungsi Autonomi dan Integratif – Batang Ptak • pons • medulla oblongata • Otak tengah – Serebellum – Thalamus, Hipothalamus Batang Otak • The “lower brain” – medulla oblongata – pons – midbrain • Fungsi: – homeostasis – Koordinasi Pergerakan – Konduksi Impuls ke Pusat Otak Medulla oblongata & Pons • Kontrol Fungsi Otonomi Homeostatis – Aktivitas pembuluh darah dan jantung – Pernafasan – Menelan – Muntah – Pencernaan • Relay Informasi dari dan ke Pusat Otak Otak Tengah • Terlibat dalam integrasi informasi sensori – pengendalian visual reflexes – Pengendalian informasi auditory reflexes Formasi Reticular • Tidur & pola kebugaran aktivitas elektrik di dalam otak – Dilaporkan sebagai ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) – Umumnya bermimpi terjadi selama REM (rapid eye movement) sleep satu sentimeter kubik otak manusia mengandung lebih dari 50 juta sel saraf, yang masing-masing bisa berkomunikasi dengan ribuan neuron lain dalam jaringan kerja pengolahan informasi saraf dikhususkan untuk transmisi impuls dengan cepat, secepat 150 m/detik (lebih dari 330 mil per jam) Gambaran Umum Sistem Saraf Analog dengan telepon Berfungsi Sebagai: Input Sensori Integrasi Output Motoris SISTEM SARAF ‘ Tersusun atas Neuron dan selsel pendukung SISTEM SARAF Sel Saraf atau Neuron adalah Unit Dasar Komunikasi pada sistem saraf Vertebrata Komponen Sistem Saraf Tiga Kelas Neuron • Sirkuit Neural Terdiri Atas: – Sensory neurons • Reseptor rangsang – Interneuron (CNS) • Integrasi sinyal – Motor neuron • Transfer sinyal ke efektor (muscle) Tipe Neuron dalam Sistem Saraf Anatomi Neuron • Cell body: Bagian Fungsional • Dendrites: Ekstensi Pendek Penerima sinyal • Axon: Ekstensi Panjang yang menerima impuls NEURON Bagaimana Kerja Neuron Memegang dan Menggerakan Info? • Neuron pada waktu istirahat memiliki voltase berbeda dengan neuron menembus membran plasma, disebut “resting voltage potential” • Potensial Aksi(PA) terjadi apabila muatan menembus membran yang berubah secara singkat • Potensial Aksi bergerak ke bawah membran dengan cepat. • Potensial aksi dapat bergerak lebih cepat pada bagian yang bermyelin, disebut “saltatory conduction” Neuron Bermyelin Na+ Na+ K+ A. Polarisasi Na+ K+ K+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ K+ K+ Na+ Na+ K+ Na+ K+ K+ C.Repolarisasi Na+ ACh Na+ B. Depolarisasi Na+ K+ K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ Gb. Muatan Elektrik dan Konsentrasi Ion pada Sarcolemma Table 7–1 State or Event Description Resting Potential Polarization • Sarcolemma has a () charge outside and a () charge inside. •Na� ions are more abundant outside the cell; as they diffuse inward, the sodium pump returns them outside. •K� ions are more abundant Inside the cell; as they diffuse out, the potassium pump returns them inside. Action Potential Depolarization • ACh makes the sarcolemma very permeable to Na� ions, which rush into the cell. • Reversal of charges on the sarcolemma: now () outside and () inside. • The reversal of charges spreads along the entire sarcolemma • Cholinesterase at the sarcolemma inactivates ACh. Repolarization • Sarcolemma becomes very permeable to K� ions, which rush out of the cell. • Restoration of charges on the sarcolemma: () outside and () inside. • The sodium and potassium pumps return Na� ions outside and K� ions inside. • The muscle fiber is now able to respond to ACh released by another nerve impulse arriving at the axon terminal. SIFAT SINYAL SARAF DENDRIT IMPULS AKSON Impuls adalah sinyal listrik yg bergantung pada aliran ion yang menembus membran plasma neuron. Potensial Membran disebabkan oleh perbedaan konsentrasi ion antara isi sel dengan cairan ekstraselluler Impuls Saraf adalah Sinyal Bioelektrik • Pompa Sodium-Pottasium menggunakan ATP untuk mentransport ion sodium ke luar dan ion pottasium masuk ke dalam membran • Pada waktu neuron beristirahat memiliki muatan negatif relatif terhadap keadaan di luar membran • Potensial aksi reversal dan restorasi muatan berbeda yang menembus membran • Pompa sodium-potassium dapat menyimpan kembali persebaran original ion-ion • Potensial Aksi adalah “all-or-none events” Mempertahankan Resting Membrane Potential Resting Membrane Potential, Graded Potentials, and an Action Potential Transfer Informasi dari Neuron ke Target • Synaptic transmission: – Mengeluarkan neurotransmitter: menaikan potential • Pengaruh neurotransmitter: – Excitatory: depolarisasi sel postsynaptic – Inhibitory: hiperpolarisasi sel postsynaptic • Peran postsynaptic neuron: integrasi dan proses informasi Lokasi Reseptor Akson Neuron Presynaptic Inaktivator (Cholinesterase) Vesicle Neurotransmitter Na+ Na+ Na+ Dendrit Neuron Postsynaptic Mitokondrion Neurotransmitter (Acetylcholin) Neurotransmitter yang teraktivasi Gb. Impuls Transmisi pada Synapse Tipe Kimiawi synapse • Acetylcholine: neuromuscular junctions, kelenjar, otak dan spinal cord • Norepinepherine: mempengaruhi bagian otak berkaitan dengan emosi dan mimpi Jalur Aliran Informasi • Sinyal di antara Otak dan Spinal Cord bergerak ke bagian tubuh melalui sel saraf • Sensory nerves :sinyal bergerak ke arah Otak dan Spinal Cord • Motor neurons: menggerakkan sinyal dari Otak atau Spinal Cord ke Bagian tubuh Pembagian Sistem Saraf • Sistem Saraf Pusat (Central nervous system) • Sistem Saraf Tepi • CNS • PNS • Otak dan Spinal Cord • Semua saraf yang membawa sinyal ke dan dari CNS (Peripheral nervous system) Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Interneuron Central canal Synapse Cell body of sensory neuron Dendrite of sensory neuron Gray Matter Ventral root Receptor Axon of motor neuron Cell Body of Motor Neuron Synaptic knobs Effector muscle Gb. Cross-section of the spinal cord and the three types of neurons. Spinal nerve roots and their neurons are shown on the left side. Spinal nerve tracts are shown in the white matter on the right side. All tracts and nerves are bilateral (both sides). QUESTION: The dorsal column is an ascending tract, and the corticospinal tract is descending. Explain what this means. (2) Sensori Neuron Dorsal Root Ganglion (5)Quadriceps Femoris Muscle (Kontraksi) Dorsal Root (1) Stretc Receptor Stimulus Biceps Femoris Muscle (Rileks) Gray Matter Ventral Root (4) Motor Neuron (3) Synapse pada Spinal Cord Gb. Repleks Patella