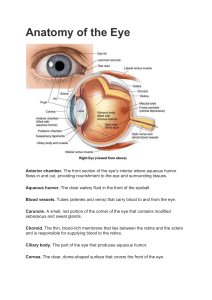
1 41. 1. 2. 3. 4. A. B. C. D. E. What basal cistern(s)contain portions of the vein of Rosenthal ? Crural Quadrigeminal Ambient Quadrigeminal 1,2,3 are correct 1 and 3 are correct 2 and 4 are correct Only 4 is correct All of the above Scenario: A 45 year old male undergoes a subtemporal approach for tumor resection with elevation of the dura from the middle fossa floor and petrous bone. 42. Structures visible on the floor of the middle cranial fossa during this exposure may include all of the following EXCEPT? a. Middle meningeal artery b. N. V3 c. Lesser superficial petrosal nerve d. N. XII e. Greater superficial petrosal nerve 43.Postoperatively, the patient has decreased lacrimation on the ipsilateral side. What is the most likely etiology of this problem? a. Lesser superficial petrosal nerve b. Greater superficial petrosal nerve c. Geniculate ganglion injury d. Chorda tympani injury e. Injury of Jacobson’s nerve Answer: B TRAUMA 1. Most common cause of death in a patient of head injury is A. Raised ICP B. Hemorrhage C. Coma D. Respiratory complication 2.Which type of seizure among the following does not follow head trauma A. Absence (petitmal) B. Partial complex, psychomotor variety C. Partial motor with Jacksonian march D. Partial motor with secondary generalization 2 3. The least frequent site for traumatic SAH is A. Convexity B. Basal cistern C. Tentorial edge D. Sylvian fissure/Interhemispheric 4. The following is the brain CT scan. Why does the patient have same side hemiparese with the hematoma ? a. Shift of the brainstem away from the mass producing compression of the contralateral cerebral peduncle against the tentorium b. The patient likely suffered a Duret hemorrhage c. There was likely a contusion in the underlying motor cortex on the contralateral side that was not detected on the initial ct scan d. The patient likely had a left internal caotid artery dissection that subsequently showered emboli to the distal vasculature e. There was an associated fracture of the transverese foramen on the left, which produced a vertebral artery disection and small infarct in the ventral pons Answer : A 7. A 22 year old male is brought to the emergency department after sustaining injuries in a motor vehicle collision. The patient has a heart rate of 122, respiratory rate of 28, SBP of 86, oxygen saturation of 88% and mild tracheal deviation to the left. What is the immediate next step in management of this condition? A. emergent needle thoracosinthesis B. placement of thoracostomy tube C. Portable chest –ray D. Obtain an arterial blood gas E. CT scan of the chest Answer: A 3 8. An 18 year old male suffers a moderate closed head injury with a concomitant fracture of the skull base. The patient exhibits prominent meningeal signs with a fever and leukocytosis one week after the injury. Which of the following organisms is the most likely to be identified on CSF culture? A. Haemophilus influenzae B. Moraella catarrhalis C. Strep. Pneumoniae D. Klebsiella pneumonia E. Staph. Epidermis Answer: C 9. The most likely etiology of the lesion depicted below in this gross specimen? A. Direct contusion B. Shearing injury C. Herniation D. Arterial dissection E. Arterial rupture Answer: C 10. Metabolic responses to trauma include each of the following except A. hypoglycemia B. increased rate of lipolysis C. increased Na+ reabsorption D. increased water reabsorption E. metabolic'alkalosis Answer: A 12. Each of the following is true of diffuse brain swelling except that it is A. a result of cerebrovascular congestion B. a result of cytotoxic edema C. associated with a 50% mortality rate in severely head-injured children 4 D. manifested on computed tomography (CT) scan by a compression of the perimesencephalic cistern E. more common in children than in adults Answer: B 14. The most common acid-base disturbance in mild to moderately injured patients without severe renal, circulatory, or pulmonary decompensation is A. respiratory acidosis and metabolic alkalosis B. respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis C. respiratory or metabolic acidosis D. respiratory or metabolic alkalosis Answer: D 15. The intracranial hypertension after trauma is maximum between A. 0 – 24 hr B. 24 – 48 hr C. 48 – 72 hr D. 72 – 96 hr Answer: C 16. Among all the factors in GCS the most PROGNOSTIC is A. Verbal response B. Eye opening C. Motor response D. All of the above Ans. C. 19. 20 years old women came to the emergency unit at your hospital with GCS score 4, dilatation of pupil dan light reflex negative, MAP 90 mmHg, after the rescucitation, GCS increase until 6, but right superior extremity did not move pain stimulation, pupil still dilated and light reflex still negative. What will you do next if you are on duty on that day : a. Give a mannitol after fluid rescucitation and placed the catheter because there is a clinical sign of increased of ICP from the lateralization. b. Performed Head Computed Tomography after cervical, thoracal x-ray and physical examination. c. Hiperventilation because there is a sign of increases of ICP of lateralization d. Give an intravenous fluid with cold normal saline to cover the hypermetabolism e. Check of the blood routine, RFT, LFT and urinary Answer : B 20. According from the story above, which side of the brain that possibly found with hematoma ? a. Anterior b. Posterior c. Right side d. Left side 5 e. Caudal Answer: D 22. The first priority in the overall assessment of a trauma patient with an acute cervical spine fracture is: A. Ongoing hemorrhage B. Neurological deficit C. Spinal instability D. Blood pressure E. Airway integrity SPINE 21. In the spine, which tumor is most commonly located in an intradural/extremedullary location: A. Astrocytoma B. Hemangioblastoma C. Ependymoma D. Adenocarcinoma E. Schwannoma 24. The right vertebral artery is injured during posterior C1-2 transarticular screw fixation, while placing the first screw. The MOST appropriate surgical management strategy is: A. Place the left screw B. Remove the right screw C. Extend the fusion to the occiput D. Use only right sided instrumentation E. none all above 25. What is the most common adverse event following laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelophaty? A. Loss of cervical range of motion B. C5 root palsy C. Inadequate cord decompression D. Progressive cervical kyphosis E. Accelerated adjacent level deterioration 26. What is the recomended insertion torque for halo pins in adults? A. 8 inch pounds B. 6 inch pounds C. 4 inch pounds D. 10 inch pounds E. 12 inch pounds 27. What radiographic finding is a contraindication to cervical laminoplasty? A. Spinal cord signal change 6 B. Ossified posterior longitudinal ligament (OPPLL) C. Multilevel cervical spondylosis D. Cervical kyphosis E. Congenital cervical stenosis 28. According to the guidelines for the Performance of Fusion Procedures for Degenerative Disease of the Lumbar Spine, the literature supports the use of fusion in lumbar decompression surgery for degenerative stenosis when associated with: A. Conjoined nerve root B. Focal disc herniation C. Spondylolisthesis D. Spina bifida E. Congenital stenosis 29. A normal intraoperative electromyographic study during lumbar fusion surgery has been shown to the BEST corelate with: A. Improved fusion rates B. Improved patient outcomes C. Lack of a neurological injury D. Pedicle fractures E. none of the above 30. A twenty four years old woman present with right arm and leg weakness and left cranial nerve VI palsy following a high-speed motor vehicle accident. Her lateral cervical spine x-ray shows upper cervical prevertebral soft tissue swelling and a basion-dental interval of 16 mm. Her head CT is negative for intracranial hemorrhage. What is the recommended treatment of this injury? A. In situ arthrodesis and immobilization in a 4-poster brace B. Traction followed by immobilization in a halo C. Immobilization in a hard collar D. Internal fixation and arthrodesis E. Emmobilization in a halo 31. Based on published medical evidence review, discography may BEST be used as a diagnostic test for which clinical purpose? A. Functional Imaging relevant to patient selection for lumbar fusion B. Repair of annular tears C. Visualization of clinically relevant disc space abnormalities D. Prediction of outcome following lumbar interbody fusion E. Diagnosis of discogenic low back pain 32. After a type II odontoid fracture, the function of which ligament/membrane most strongly influences treatment options: A. Alar B. Tectorial 7 C. Apical D. Transverse E. Anterior longitudinal 33. A 27 year old sustains a Type II odontoid fracture. He is complaining of upper cervical pain, but his neurologic exam is normal. Which of the following factors would increase his risk for nonunion? A. Age less than 30 years B. Comminution of the dens C. Anterior displacement of 3 mm D. Basilar Skull fracture E. Vertebral artery injury 34. A 28 year old male presents to the Emergency Department with complaints of severe low back and right leg pain after injury while working as a carpenter the previous day. He denies weakness, numbness and gait or bowel/bladder disturbance. Examination reveals trace weakness of dorsi-flexion on the right associated with pain. The BEST Initial management strategy for this patient is: A. Epidural steroid injection B. Seven day course of bed rest C. Lumbar discectomy D. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications E. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion 35. Which of the following fractures has the poorest prognosis for healing without surgical intervention? A. hangman's B. Jefferson's fracture with 4 mm displacement of lateral masses C. type I odontoid D. type II odontoid E. type III odontoid 36. Lateral recess stenosis in spondylosis is most commonly caused by A. disk herniation B. hypertrophied pedicles C. inferior articular facet hypertrophy D. ligamentum flavum hypertrophy E. superior articular facet hypertrophy 37. Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord is caused by a deficiency of A. cobalamin B. folic acid C. nicotinic acid D. pyridoxine E. thiamine 8 40. A 35 year old woman presents with progressive upper and lower extremity myelopathy. MR imaging reveals a well-defined, contrast enhancing lesion 2 cm in diameter in her cervical spinal cord. What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient? A. Open biopsy of the lesion followed by appropriate chemotherapy and radiotherapy B. CT guided biopsy followed by appropriate chemotherapy and radiotherapy C. Serial MR imaging every three months D. Complete surgical excision of the lesion, if possible E. none of the above 44.During surgery, additional exposure is needed to access the upper petroclival region for tumor resection. Which maneuver may assist the surgeon in accomplishing the task? a. Further drilling of Glassock’s traingle b. Additional exposure through Kawase’s quadrilateral c. Further drilling of the arcuate eminence d. Identifying Trautmann’s triangle an eposing medially to this landmark e. Modifying the approach by utilizing a presigmoid corridor Answer: B 45.Which of the following meningioma variants is associated with more aggresive clinical behaviour? a. Papilary b. Angiomatous c. Chordoid d. Clear cell e. Metaplastic Answer: A 46.What is the most common chromosomal abnormality associated with meningiomas ? a. Allelic loss of 1p b. Monosomy 22 c. Allelic loss of 10 d. Allelic loss of 22q e. Monosomy 2 Answer: B 47.Which of the following meningioma variants is a WHO grade II neoplasm? a. Psammomatous b. Microcystic c. Papillary d. Secretory e. Clear cell Answer: E 48. Which approach is favored for a patient with an 8 mm acoustic neuroma in which hearing preservation is a goal? 9 A. middle fossa B. suboccipital C. translabyrinthine D. transcochlear E. retrosigmoid Answer: A 49. The single most important factor in the recurrence of meningiomas is A age of the patient B. bone invasion C. histologic type of benign meningioma D. postoperatiye tumor residual E. sex of the patient Answer: D 50. In the infratentorial supracerebellar approach to the pineal region, which of the following veins are usually sacrificed? I. superior vermian vein 11. posterior pericallosal vein Ill. precentral cerebellar vein IV. basal vein of Rosenthal A. I, 11,111 B. I, 111 C. 11, IV D. IV E. all of the above Answer: B 51. Cerebral salt wasting and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) may best be distinguished by measuring A. plasma arginine vasopressin (AVP) B. serum osmolality C. serum sodium D. urine sodium E. volume status Answer: E 52.The most common finding on audiography in patients with acoustic neuromas is A. flat loss B. high-frequency loss C. low tone loss D. normal audiogram E. trough-shaped loss Answer: B 10 53. This patient is most likely to present A. congestive heart failure B. fever and chills C. headaches D. hemiparesis E. subarachnoid hemorrhage 54. A. B. C. D. E. AVM carotid occlusion dural AVM meningioma moyamoya disease 55. Which of the following is not typically seen in neurofibromatosis type 2? A. acoustic neuromas B. caf6 au lait spots C. cutaneous neurofibromatosis D. Lisch nodules E. plexiform neurofibromas 56. Catecholamine production can occur in which of the following tumors? A. choriocarcinomas B. glomus jugulare tumors C. oligodendrogliomas D. pineocytomas E. pleomorphic xanthoastrocytomas 11 57. Cushing's syndrome is most often associated with a(n) A. acidophilic pituitary adenoma B. basophilic pituitary adenoma C. chromophobic pituitary adenoma D. ectopic source of adrenocorticotropic hormone (AaH) E. nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma 58. What lesion is shown in this picture? A. epidermoid B. lipoma C. metastatic tumor D. multiple sclerosis E. teratoma 59. Most patients with intrinsic brainstem gliomas initially present with A. cranial neuropathies B. headache C. hydrocephalus D. nausea and vomiting E. papilledema 60. ''Trilateral retinoblastoma" describes bilateral ocular retinoblastomas and a(n) A. astrocytoma B. medulloblastoma C. neurofibroma D. optic nerve sheath tumor E. pineoblastoma 61. The most common primary benign tumor of the adult orbit is (a) A. cavernous hemangioma B. dermoid cyst C. lymphangioma D. optic nerve glioma E. sarcoidosis 62. 12 A. B. C. D. E. corpus callosum lipoma craniopharyngioma giant aneurysm glioblastoma multiforme growing skull fracture 63. A. B. C. D. E. aqueductal stenosis brainstem astrocytoma Chiari malformation pituitary tumor polymicrogyria 64. A. B. C. D. craniopharyngioma chordoma pituitary adenoma Rathke's cleft cyst 65. Which of the following is not characteristic of ependymomas? A. blepharoplasts in the basal cytoplasm 13 B. intermediate filaments that are immunohistochemically identical to glial filaments of astrocytes C. perivascular pseudorosettes D. surface microvilli E. true rosette formation 66. Each of the following is true of gangliogliomas except that A. The astrocytes are GFAP positive. B. The ganglion cells are synaptophysin positive. C. They contain neuropeptides. D. They are usually diffusely infiltrative. E. They are most common in the temporal lobes. 67. 1. 2. 3. 4. A. B. C. D. E. Which of the following neoplasm is/are associated with von Hippel Lindau syndrome? Pheochromocytoma Renal cell carcinoma Cerebellar hemangioblastomas Endolymphatic sac tumors 1,2,3 are correct 1 and 3 are correct 2 and 4 are correct Only 4 is correct All of the above 68. What is the most common chromosome involved with cytogenic abberations in glioblastoma multiforme? a. Chromosome X b. Chromosome 11 c. Chromosome 10 d. Chromosome 7 e. Chromosome 22 69.Primarily branches of what nerves innervate the supratentorial dura? 1. Upper cervical spinal nerves 2. Glossopharyngeal nerve 3. Vagus nerve 4. Trigeminal nerve A. 1,2,3 are correct B. 1 and 3 are correct C. 2 and 4 are correct D. Only 4 is correct E. All of the above 70. What is the primary ligand that binds to epidermal growth factor receptor EFGR in gliomas? A. Fibronectin 14 B. Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) C. Tumor Growth Factor (TGF-ά) D. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) E. Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) 71. Arteri Khoroidalis anterior memberikan suplai berikut dibawah ini, kecuali : A. Amygdala B. globus pallidus C. Hippocampus D. Kapsula Interna E. Hypothalamus 72. Semua hal di bawah ini adalah benar mengenai ICA, kecuali : A. Arteri itu memasuki tengkorak melalui tulang sphenoid B. Arteri ini berada didalam sinus kavernosus C. Arteri ini mempercabangkan cabang – cabang ke kapsula interna D. Arteri ini mempercabangkan arteri khoroidalis anterior E. Arteri ini mempercabangkan arteri hipofisis superior 73. Thalamus mendapatkan perdarahan dari : I. Arteri khoroidalis posterior medial II. Arteri Khoroidalis anterior III. Arteri basilaris IV. Arteri cerebri media A. I,II,III B. I,III C. II,IV D. IV E. Semua benar 74. Berikut adalah lokasi perdarahan otak paling sering a. Pons b. Thalamus c. Putamen d. Lobar e. Cerebellum Jawaban C 75.Kapsula interna bagian depan diperdarahi oleh a.Arteri choroidalis anterior b.Arteri rekuren Heubner c.Arteri tuberoinfundibular d.Arteri basilaris e.Arteri PICA Jawaban B 15 76. Pasokan darah ke anggota bagian belakang dari kapsul dalam berasal dari : A. Arteri koroidal anterior B. Arteri inferolateral C. Arteri Heubner rekuren D. Arteri tuberoinfundibular E. Arteri basilaris 77. Wanita 35 tahun menerima transplantasi hati mengalami tanda rangsang meningeal dan demam. Hasil pemeriksaan cairan CSF menunjukkan bahwa terdapat infeksi jamur. Penyebab mengitis jamur tersering adalah? A. Aspergillus B. Candida C. Mucor D. Cryptococcus E. Rhizopus 78. Selama pendekatan subtemporal ekstradural apabila seseorang mengebor tulang petrosus temporal pada area di sebelah medial terhadap foramen spinosum, posterior terhadap foramen ovale dan dibawah GSPN. Struktur apakah yg ditemukan ? A. Arteri karotis interna B. Saraf trigeminal C. Saraf abdusens D. Kokhlea E. Arteri vidian 79. Faktor resiko paling signifikan untuk perdarahan dari fistula arteriovenosus dura adalah : A. Ukuran B. Lokasi C. Restriksi vena outflow D. Drainase vena kortikal E. Semua benar 80. You are carring for a child who was born with a myelomeningocele. The family is aware that these children are more prone to latex allergies and has ask you to address spesific questions regarding this issue. Which of the following statements is CORRECT in regard to latex allergy in children with spina bifida? A. Latex directed antibodies are found aproximatelly 50% of children with myelomeningoceles. B. If a child with myelomeningocele has a negative Latex skin test at the time of birth, this child will not develop a Latex allergy. C. All children with myelodisplasia will eventually develop Latex allergy. D. A normal sibling of a child with myelodisplasia is also at an increased risk to develop Latex allergy. E. If myelodisplastic child requires frequent, daily blader catheterizations, but is not latex allergic, then this child should continue to use latex catheters for catherization purpose. 16 A. Latex directed antibodies are found aproximatelly 50% of children with myelomeningoceles. 81. An 11- year- old girl is referred to neurosurgery from the urology clinic with severe episodes of urinary tract infection during the past several years. Recently she has noticed an ulcer at the tip of her right big toe which is not healing. During the past few months she has had a few episodes of nocturia. Upon physical examination she had a big patch of hair near her second and third lumbar spinous processes. She had a slightly lax anal sphincter and was unable to walk on toes and heels on the right side. Deep tendon reflexes were slightly up at the knees and left ankle but absent at right ankle. Sensation to pin prick was down on right side from L5 to S4 and on L3 to S1 and anteroposterior (AP) measurement of 25-35 mm. MRI indicated a mass measuring 3 cm x 2 cm x 7 cm in the spinal canal which was hyperintense in T1-weigthed images. The position of the epicomus was at the level of L2. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis ? A. Myxopapillary ependymoma of filum terminale B. Astrocytoma of conus with central degeneration C. Tethered cord with lipoma D. Sacrococcygeal teratoma C. Tethered cord with lipoma 82. a. b. c. d. During surgery for the spinal lipomas, one SHOULD EXPECT to find the dorsal nerve roots : running within the fatty mass immidiately dorsal to the enterance of the fatty stalk into the spinal cord along the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the fatty mass immediately ventrolateral to the fatty stalk as it enters the spinal cord D. immediately ventrolateral to the fatty stalk as it enters the spinal cord 83. A 7-year-old boy presents with a two month history of progressive headaches, vomiting, and ataxia. On examination he is sleepy but easily aroused and readily verbalizes appropriately and follow commands. His pupils are equal and reactive but he has impaired upward gaze. Funduscopic exam reveals bilateral papiledema. Based on the clinical symptoms, exam, and MRI, the MOST LIKELY diagnosis is : a. cerebellar astrocytoma b. brainstem glioma c. hemangioblastoma d. primitive neuroectodermal tumor (meduloblastoma) e. cavernous angioma D. primitive neuroectodermal tumor (meduloblastoma) 17 84. A 7-year-old boy presents with a two month history of progressive headaches, vomiting, and ataxia. On examination he is sleepy but easily aroused and readily verbalizes appropriately and follow commands. His pupils are equal and reactive but he has impaired upward gaze. Funduscopic exam reveals bilateral papiledema. proper staging for this disease should include all EXCEPT: a. CSF for a-fetoprotein b. CSF for cytology C. bone marrow biopsy c. postoperative head MRI with and without contrast d. MRI of the spine with and without contrast e. CSF for a-fetoprotein 85. The most common presenting symptom of neonates with vein of Galen aneurysms is: A. congestive heart failure B. hydrocephalus C. intracerebral hemorrhage D. seizures E. subarachnoid hemorrhage A. congestive heart failure 86. Trigonocephaly results from premature closure of the: A. coronal suture bilaterally B. coronal suture unilaterally C. frontosphenoidal suture D. lambdoid suture E. metopic suture E. metopic suture 87. Approximately what percentage of infants with myelomeningocoele have magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evidence of a Chiari II malformation? A. 20% B. 40% C. 60% D. 80% E. 100% E. 100% 18 88. Autosomal recessive inheritance A. Apert's syndrome B. Crouzon'sdisease C. Both D. Neither D. Neither 89. Each of the following is true of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) in the newborn except A. Periventricular hemorrhagic infarction is one sequela. B. Posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus can result in persistent bradycardia and apneic spells. C The capillary bed of the germinal matrix is composed of large irregular vessels. D. The germinal matrix is the most common site of IVH in the full-term neonate. E. The risk of IVH is greater in the preterm than in the term infant. D. The germinal matrix is the most common site of IVH in the full-term neonate. 90. The most common single-suture synostosis is A. coronal B. lambdoid C. metopic D. sagittal E. Sphenozygomatic D. Sagittal 91. The essential difference between a syringomyelic and a hydromyelic cavity is that the cavity in A. hydromyelia is lined with ependymal cells, and in syringomyelia is not B. hydromyelia is lined with choroid plexus, and in syringomyelia is not C. syringomyelia contains CSF, and in hydromyelia contains serum D. syringomyelia is focal, and in hydromyelia is more extensive E. syringomyelia is an enlargement of the central canal, and in hydromyelia is an enlargement of the anterior median septum A.hydromyelia is lined with ependymal cells, and in syringomyelia is not 92. Trilateral retinoblastoma" describes bilateral ocular retinoblastomas and a(n) A. astrocytoma B. medulloblastoma C. neurofibroma D. optic nerve sheath tumor E. Pineoblastoma 19 E. pineoblastoma 93. Closure of the caudal neuropore Postovulatory Day Number A. 13 B. 17 C. 22 D. 24 E. 26 E. 26 94. Contains the choroid plexus at the foramen of Luschka A ambient cistern B. cerebellopontine angle cistern C. interpeduncular cistern D. lateral cerebellomedullary cistern E. prepontine cistern D. lateral cerebellomedullary cistern 95. A new born child has seizure and overt heart failure. The child was well at the time of her birth. The anterior fontanelle is now full. A CT scan demonstrates hydrocephalus and a malformation (Figure 39). Based on the clinical history and CT finding, the MOST LIKELY diagnosis is: a. Tectal glioma b. Giant basilar aneurysm c. Vein of Galen fistula d. Hydrocephalus from obstructive pineal tumor e. Brain abcess C. Vein of Galen fistula 96. A 6-year-old boy is admitted to the hospital with an open depressed skull fracture at the vertex of he head. CT confirms the presence of displaced bone in the region of the superior sagittal sinus. Two hours following the injury, the child is admitted to the hospital. He is awake, and alert, but somewhat irritable, without focal neurological deficits. He is maintain in a sitting position but has a continual minimal seepage of blood and CSF from a3-cm scalp laceration. Very ild papilledema is seen by a neurology resident. There is no fever or meningismus. The hematocit is 36. You SHOULD: a. Treat conservatively with antibiotics after closure of the skin laceration. 20 b. Operate immediately for elevation ef the depressed skull fracture and to eliminate CSF leakage and contamination. c. Perform angiography or venography to identify the extent of sagittal sinus patency; if the sinus is noted to be preserved, treat the child conservatively with antibiotics and Diamox d. Begin operative treatment when the entire operating team is ready to deal with potential massive hemorrhage e. Treat conservatively with antibiotics and lumbar drainage D. Begin operative treatment when the entire operating team is ready to deal with potential massive hemorrhage 97. 4-month-old baby boy presents to your office for an abnormally shaped head. The infant tends to hold his head turned to the right and has a flat occiput on the right. The right ear is anterior to the left in the axial plane and the right forehead is more prominent than the left, as is the malar eminence on the right. What is the CAUSE of this abnormality? A.skull molding B.sagittal suture stenosis C.right lambdoid suture stenosis D.left lambdoid suture stenosis E.coronal suture stenosis A.skull molding 98. A 12-year-old girl has had sudden onset of weakness punctuated by partial seizures with secondary generalization. She has had normal development and has been healthy all of her life, although her parents note that she had a fever and pharyngitis about Wi weeks prior to the onset of the current illness. The physical exam reveals a stuporous child with spastic quadriparesis and right seventh cranial nerve palsy. Analysis of CSF reveals 55 white cells, all lymphocytes and monocytes, and 3 red cells. The protein is slightly elevated but the glucose is normal. An MR was obtained and is depicted in Figure 59. The MOST LIKELY diagnosis is: a. multiple sclerosis b. acute disseminated encephalomyelitis c. systemic lupus erythematosus d. tuberculous meningitis B.acute disseminated encephalomyelitis 99. Postoperative shunt infections are most commonly caused by 21 A. coagulase-negative staphylococci B. H. influenzae C. Pseudoqonas species D. S. aureus E. S. Pneumoniae A.Coagulase-negative staphylococci 100. All of the following are seen in Sturge-Weber syndrome except A. calcified cortical vessels B. facial nevus contralateral to seizure activity C. hemisensory deficit contralateral to facial nevus D. meningeal venous angiomas E. tramline calcifications outlining the convolution of the parieto-occipital cortex C.calcified cortical vessels Skull films may reveal "tramline calcification" is present in the parieto-occipital cortical substance, not the vessels. 101. Bulbus jugulari merupakan tempat bermuara dari : A. sinus petrosus posterior B. sinus petrosus inferior C. sinus sigmoid D. sinus sagitalis E. sinus rectus 102. Organisme yang paling sering ditemukan pada abses cerebri : A. Staphilococcus B. Streptococcus C. Pseudomonas D. Klebsiella E. Listeria 103. Organisme yang paling sering ditemukan pada subdural empyema pada bayi : A. Hemophilus B. Listeria C. E. Coli D. Staphilococcus E. Pseudomonas 104. Most cases of idiopathic hemifacial spasm are thought to result from A. ephatic transmission B. Hypersensitivity of facial muscle 22 C. Hypocalcemia D. Psychiatric disorders E. Recurrent of laten viral infection 105. Surgical therapies used for dystonia have traditionally included all of the following EXCEPT? A. Peripheral denervation B. Pallidotomy C. Thallamotomy D. Dorsal column stimulation E. Motor cortex stimulation 106. A 17-year-old girl develops mild dementia, tremor, and rigidity. Her father died in his fourth decade of life of a progressive dementing illness associated with jerking (choreiform) limb movements. On exposure to L-dopa, she becomes acutely agitated and has jerking limb movements A. Alzheimer’s disease B. Parkinson’s disease C. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease D. Vitamin B12 deficiency E. Huntington’s disease 107. A 17-year-old male presents with 10 days of progressive tingling paresthesias of the hands and feet followed by evolution of weakness of the legs two evenings before admission. He complains of back pain. He has a history of a diarrheal illness 2 weeks prior. On examination, he has moderate leg and mild arm weakness, but respiratory function is normal. There is mild sensory loss in the feet. He is areflexic. Mental status is normal. The most frequent preceding infection before the onset of this syndrome is a. HIV b. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) c. Chlamydia psittaci d. Mycoplasma pneumoniae e. Campylobacter jejuni Jawab:E 108. Pasien dengan riwayat mastoidectomy mengalami afasia. Pemeriksaan CT scan menunjukkan abses serebri. Dimanakah lokasi kemungkinan abses ini ? A. Lobus frontal B. Lobus temporal C. Lobus parietal D. Lobus occipital 109. Baik infeksi HIV maupun CMV pada otak memproduksi A. Nodul microglia B. Intranuclear bodies C. Intracytoplasmic bodies D. 23 E.