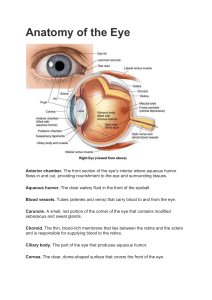
Nama : 1. While performing an axillary brachial plexus block, all of the following nerves are spared, except A. Musculocutaneous nerve B. Ulnar nerve C. Lateral brachial cutaneous nerve D. Medial brachial cutaneous nerve 2. The most correct statement regarding the appropriate use of ultrasound equipment during performance of regional anesthesia is A. Higher frequency ultrasound probes are used for deeper penetration B. High-frequency ultrasound probes provide for higher image resolution C. Liner array probes are typically used for imaging deeper anatomical structures D. The curvilinear probe is designed to best image superficial structures 3. Which of the following nerves is typically spared during performance of an interscalene brachial plexus block? A. Median B. Axillary C. Musculocutaneous D. Ulnar 4. A supraclavicular block of the brachial plexus does not provide consistent surgical anesthesia for shoulder surgery secondary to potential sparing of which of the following nerve branches of the brachial plexus? A. Musculocutaneous and axillary nerve branches B. Axillary and suprascapular nerve branches C. Ulnar and axillary nerve branches D. Suprascapular and supraclavicular nerve branches 5. Performing an infraclavicular approach for brachial plexus blockade would deposit local anesthetics at which of the following anatomical levels of the plexus? A. Trunks B. Divisions C. Cords D. Roots 6. A supraclavicular approach for brachial plexus blockade would deposit local anesthetics at which of the following anatomical levels of the plexus? A. Branches B. Trunks/Divisions C. Cords D. Roots 7. When performing an axillary block of the brachial plexus for distal upper extremity surgery, which of the following nerves most often needs to be targeted separately? A. Ulnar B. Radial C. Musculocutaneous D. Median 8. Anatomical location of the musculocutaneous nerve in the upper forearm is most frequently found within which of the following muscles? A. Triceps brachii B. Biceps brachii C. Coracobrachialis D. Brachialis 9. At what time frame following the postsurgical period does persistent postsurgical pain become defined as being “chronic pain”? A. 1 to 2 weeks B. 3 to 4 weeks C. 1 to 2 months D. 6 to 12 months 10. Type(s) of symptomatic pain conditions that best describes “chronic” pain often includes A. Neuropathic pain alone B. Nociceptive pain alone C. Neuropathic or nociceptive pain D. Somatic or visceral pain 11. At what levels does the modulation of pain by electrical stimulation result in the activation of inhibitory fibers? A. Nociceptor level alone B. Spinal cord level alone C. Only within the brain D. All of the above 12. Incorrect statement related to the definition of an abnormal sensation is A. Dysesthesia is an abnormal sensation with or without a stimulus B. Paresthesia is abnormal sensation without a stimulus C. Neuralgia is due to abnormality in nerve roots D. Hyperesthesia is an abnormal sensation of exaggerated response to mild stimulation 13. Which of the following clinical diagnoses best describes deafferentation pain? A. Herniated disk B. Amputation C. Neuropathic pain D. Diabetic neuropathy 14. Gasserian ganglion block is most commonly used for neuropathic pain located in which of the following nerve distributions? A. Facial nerve B. Trigeminal nerve C. Glossopharyngeal nerve D. Vagal nerve 15. All the following are inhibitory neurotransmitters in the pain pathway, except A. Norepinephrine B. Adenosine C. Serotonin D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide