(prokaryotes) viruses attack eukaryotic cells.
advertisement

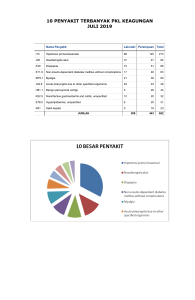
Viruses Contoh Gambar Virus Cacar : Gambar strukturnya : Ciri-ciri : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Bersifat aseluler Hanya memiliki salah satu asam nukleat (RNA atau DNA) Berupa hablur (kristal) Bentuk virus : oval, silinder, polihedral dan komplek ( ct. bakteriofag) Ukuran : Reproduksi : Litic dan lisogenik Peranan virus bagi kehidupan a. Virus yang merugikan (manusia,tumbuhan dan hewan). b. Virus yang menguntungkan SEJARAH VIRUS Ilmu tentang Virus disebut Virologi. Virus (bahasa latin) virion yang berarti racun Virus adalah organisme aselular (bukan sel) yang tidak memiliki organel-organel. Sejarah Penemuan Virus 1. Edward Jenner (1749-1823) adalah ilmuwan pertama yang berhasil menemukan vaksin mencegah penyakit cacar (variola). Penyakit cacar (variola) disebabkan virus. 2. Louis Paster adalah ilmuwan Perancis yang berhasil menemukan pusat infeksi penyakit terdapat pada otak dan medula spinalis. Selain itu, ia juga mampu memindahkan infeksi tsb ke hewan percobaan di dalam laboratorium. 3. Adolf Meyer (jerman), 1883 adalah ahli mikrobiolog bahwa : Daun tembakau berbintik-bintik kuning organisme lebih kecil dari bakteri. Buktinya : menyemprotkan getah tanaman yang sakit ke tanaman yang sehat ternyata tertular. 4. Dimitri Ivanowsky (Rusia), 1893. ahli botani Tanaman tembakau terkena penyakit mosaik. Kemudian menyaring melalui pori-pori yg sgt halus ternyata masih mampu menginfeksi daun tembakau. 5. M.W. Beijerinck, 1897.( Belanda) penyakit tembakau mengandung jasad hidup yang disebut virus 6. Wendell Stanley (Amerika Serikat), 1935. 7. Loffler dan Forsch (1897) ilmuwan dari Jerman Virus yang menyerang hewan yakni penyakit kuku dan mulut pada hewan ternak. 8. Reed (1900) Virus menyebabkan penyakit demam berdarah pada manusia. Penyakit disebabkan nyamuk Aedes aegypti. 9. Laidraw dan Stuart Harris (1933-1936) Menemukan virus influenza. 10.Jonas Salk (1953) menemukan vaksin pencegah penyakit polio. Viruses The Boundary of Life parasites responsible for causing many diseases in living things (herpes and HIV in humans, for example). Viruses are found everywhere. Viruses consist of a core of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA, and a protective coat of protein molecules and sometimes lipids. In isolation, viruses and bacteriophages show none of the expected signs of life. They do not respond to stimuli, they do not grow, they do not do any of the things we normally associate with life. Strictly speaking, they should not be considered "living" organisms at all. However, they are more complex than a lifeless collection of macromolecules and they do show one of the most important signs of life: the ability to reproduce at a fantastic rate but only in a host cell. Bacteriophages attack bacteria (prokaryotes) viruses attack eukaryotic cells. Viruses and bacteriophages invade cells and use the host cell's machinery to synthesize more of their own macromolecules. Once inside the host the bacteriophage or virus will either go into a Lytic Cycle - destroying the host cell during reproduction. or It will go into a Lysogenic Cycle - a parasitic type of partnership with the cell The Lytic Cycle The Lysogenic Cycle A provirus is a DNA virus that has been inserted into a host cell chromosome. A retrovirus injects the enzyme, reverse transcriptase into the cell to copy viral RNA into DNA. HIV is a retrovirus injecting the enzyme, reverse transcriptase into the cell to copy viral RNA into DNA. Viruses are host specific – a protein on the surface of the virus has a shape that matches a molecule in the plasma membrane of its host, allowing the virus to lock onto the host cell. HIV doesn’t target just any cell, it goes right for the cells that want to kill it. “Helper" T cells are HIV's primary target. These cells help direct the immune system's response to various pathogens. HIV undermines the body's ability to protect against disease by depleting T cells thus destroying the immune system. The virus can infect 10 billion cells a day, yet only 1.8 billion can be replaced daily. After many years of a constant battle, the body has insufficient numbers of T-Cells to mount an immune response against infections. At the point when the body is unable to fight off infections, a person is said to have the disease AIDS. It is not the virus or the disease that ultimately kills a person; it is the inability to fight off something as minor as the common cold. VIRUS YANG MENGUNTUNGKAN 1). Virus dapat dimanfaatkan dalam bidang rekayasa genetika (vektor mutasi gen) maupun penelitian di bidang kedokteran. 2). Virus yang digunakan untuk memproduksi interferon berfungsi untuk mencegah replikasi virus di dalam sel hospes. Interferon merupakan protein kecil yang dihasilkan oleh sel normal sebagai respon terhadap infeksi virus. 3). Virus digunakan untuk pembuatan vaksin. Vaksin adalah mikroorganisme patogen yang telah dilemahkan sehingga sifat-sifat patogenitas penyebab penyakitnya hilang, tetapi sifat-sifatnya antigenitas penimbul antibodi tetap. TUGAS Buatlah ringkasan dari materi ini Tugas dikumpulkan melalui email [email protected] (paling lambat 9 April 2015)