anatomi perbandingan vertebrata
advertisement

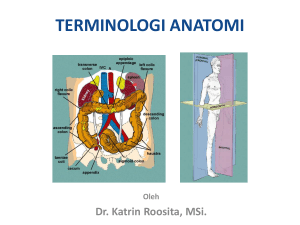
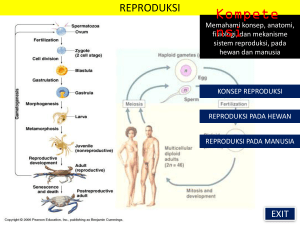
ANATOMI PERBANDINGAN VERTEBRATA Novi Febrianti SEKILAS ANATOMI • Anatomi berasal dari bahasa Yunani yang berarti memotong • Istilah-istilah anatomi berasal dari bahasa Yunani dan Latin Cabang –cabang Anatomi: • Microscopic anatomy/Anatomi mikroskopis (Sitologi, Histologi) • Developmental anatomy/Anatomi perkembangan (Embriologi) • Comparative anatomy/Anatomi perbandingan COMPARATIVE ANATOMY • Mempelajari susunan tubuh hewan vertebrata • Membandingkan susunan organ tubuh antar kelas pada sub phylum vertebrata • Tubuh hewan terbagi menjadi : - caput / chepala : kepala - collum / cervix : leher - trunchus : badan - cauda : ekor - extremitas : anggota badan bebas ^ ant / pos ^ sup / inv TERMINOLOGI • • • • • • • • • Anterior – posterior (arah) Superior – inferior (arah) Dorsal : daerah punggung Ventral : daerah perut Lateral : daerah samping / sisi Cranial : daerah kepala Caudal : daerah ekor Abdominal : daerah badan Thoracal : daerah dada (dalam dada) TERMINOLOGI • • • • • • • • Sinister : kiri Dexter : kanan Medial : daerah tengah Linea mediana : garis tengah tubuh Proximal : lebih kearah / dekat LM Distal : lebih menjauhi LM Origo : titik pangkal tidak bergerak Insersio : : menimbulkan gerak TERMINOLOGI • • • • • • Organ analog Mayor = besar Minor = kecil Pectoral : dada Pelvis : punggung bawah Bilateral simetri Simetri tubuh Dorsal Bidang simetri Bidang simetri Posterior Dorsal Ventral Simetri radial Anterior Ventral Simetri bilateral Tiga kelompok hewan triploblastik Cacing pipih Cacing gilig Mesoderm (otot) Ektoderm Ektoderm Endoderm (usus) Endoderm (usus) Mesoderm (otot) Mesenkim Aselomata Pseudoselomata Cacing tanah Ektoderm Mesoderm (otot) Selom Organ internal Endoderm (usus) Mesoderm (peritoneum) Selomata Pseudoselom Organ internal Sistem penyokong tubuh hewan Cangkang luar Tubuh lintah dibentuk oleh cairan di dalam tubuhnya Endoskeleton Eksoskeleton Sistem tubuh pada hewan Usus bagian dari sistem saluran pencernaan Saluran kelamin Otak kecil Lambung Otak sederhana dengan dua ganglion Ovarium Testis Notokorda berada di sepanjang tubuh bagian ventral Otak besar Ginjal Paru-paru Jantung Usus Pembuluh darah Eksoskeleton Kelenjar pencernaan PHYLUM CHORDATA Ciri – ciri : • Adanya dorsal tubular nerve cord, pada keadaan embrio, larva atau seumur hidup. • Mempunyai notochord, minimal pada fase embrio • Pada dinding pharynx ada lubanglubang/celah-celah pada keadaan larva atau seumur hidup (pharyngeal slits). • Mempunyai ekor Anatomy of a Chordate Subphylum Urochordata • sea squirts or tunicates • notochord present only in free-swimming larvum • notochord does not extend into head • larvum is free-swimming but non-feeding • adult is sessile filter feeder Subphylum Urochordata • sea squirts or tunicate • Campbell p 631 •Settle after brief free-swimming larvum existence. Attaches at anterior end. Metamorphosis begins. Body turns 1800. Tail, notochord, dorsal nerve cord, disappear. Subphylum Cephalochordata • “head” cord • lancelet or Amphioxus • notochord present throughout life – extends into head region • shallow marine waters • chordate characteristics developed and apparent in adult • tail has blocks of muscles called myotomes • adults resemble tunicate larvum Anatomy of a lancelet Cephalochordat a: lancelet Subphylum Vertebrata General Characteristics: • • • • chordates with a backbone exhibit cephalization closed circulatory system neural crest (p. 633) Subphylum Vertebrata Agnatha (without jaws) • lamprey – parasitic bloodsuckers w/ rasping tongue • hagfish – mainly scavengers • no paired appendages • larvum resembles lancelet Agnatha: a sea lamprey Lamprey mouth Subphylum Vertebrata Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes) • flexible endoskeletons of cartilage strengthened by calcium granules • sharks (internal fertilization) ▫ oviparous – egg laying ▫ ovoviviparous – retain fertilized eggs hatch within the uterus ▫ viviparous – young develop in the uterus • suspension-feeders (plankton) Cephalochordat a: lancelet Subphylum Vertebrata Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes) • Bottom feeders – mollusks & crustaceans • Whiplike tail w/ venomous barbs (defense) Subphylum Vertebrata Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes) • Bottom feeders – mollusks & crustaceans • Whiplike tail w/ venomous barbs (defense) Subphylum Vertebrata Osteichthyes (bony fishes) • Endoskeleton of hard calcium phosphate matrix • Operculum- protective flap • Swim bladder – controls buoyancy Seahorse Subphylum Vertebrata Amphibia (“two lives”) • first tetrapods • transition to land – still tied to water for respiration and reproduction • Gills lungs (metamorphosis) • Frogs, toads, salamanders, newts Subphylum Vertebrata Reptilia (Campbell, p. 644) (to creep) • lizards, snakes, turtles, tortoises, Gila monsters, crocodiles, alligators • first true land animal • Scales, lungs, amniotic egg • no feathers • cold-blooded – ectotherms – (energy conservation) Hatching reptile Subphylum Vertebrata Fossil links………… • Evolutionary link ?? between reptiles and birds: Archaeopteryx , a Jurassuc birdreptile • Clawed forelimbs • Teeth • Long tail w/ vertebrae Archaeoptery x Subphylum Vertebrata Aves (bird) • feathered • few flightless: ostrich, kiwi, emu • breastbone with keel – carina – permitting flight • jays, sparrows, warblers, etc Subphylum Vertebrata Mammalia (breast) • • • • • • Hair or fur of keratin Active metabolism = endothermic Efficient respiration w/ diaphragm Efficient circulation w/ 4-chambered heart Layer of fat Mammary glands, tooth differentiation Subphylum Vertebrata Mammalia (breast) • Monotremes – egg-laying mammals (Platypuses & echidnas – spiny anteaters) • Placental mammals • Marsupial mammals – kangaroo, opossum Marsupial Placental Marsupial & Placental Mammals