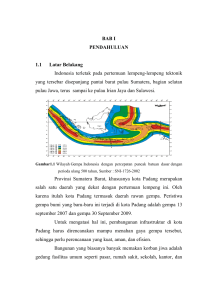
xvii INTISARI Salah satu kegagalan struktural tanah
advertisement

INTISARI Salah satu kegagalan struktural tanah akibat gempa bumi adalah likuifaksi. Likuifaksi terjadi pada lapisan pasir lepas yang jenuh air akibat menerima beban siklik dari getaran gempa bumi yang merubah sifat tanah dari keadaan padat menjadi cair sehingga tidak mampu menopang beban bangunan di dalam atau di atasnya. Untuk mengetahui pengaruh beban terhadap potensi likuifaksi dilakukan uji eksperimental. Sebuah penelitian eksperimental menggunakan alat shaking table dilakukan dengan menggunakan sampel tanah yang berasal dari pasir Kali Opak Pleret Yogyakarta. Parameter gempa yang dipertimbangkan dalam penelitian ini diantaranya percepatan maksimum gempa 0,3g, 0,35g, 0,4g dengan durasi penggetaran selama 32 detik. Pengujian dilakukan tanpa beban dan penambahan beban sebesar 0,15 t/m2, 0,31 t/m2 dan 0,46 t/m2. Nilai kerapatan relatif tanah pasir dalam pengujian berkisar antara 25 – 27 % sesuai dengan kerapatan relatif di lapangan. Alat pembacaan tegangan air pori yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah pressure tranducer dan headmeter. Evaluasi hasil dari pengujian dilakukan dengan membandingkan tegangan air pori dan tegangan efektif. Likuifaksi akan terjadi jika rasio peningkatan tegangan air pori lebih dari satu atau sama dengan satu (ru ≥ 1) sebaliknya jika ru < 1 tidak terjadi likuifaksi. Berdasarkan hasil pengujian analisa saringan, pasir Kali Opak Pleret masuk pada zona paling rentan terhadap likuifaksi. Hal yang sama ditunjukkan dari hasil pengamatan dengan mikroskop stereo, bentuk partikel pasir cederung terlihat bulat dan hampir seragam sehingga berpotensi likuifaksi. Hasil pengujian menggunakan shaking table menunjukkan bahwa semakin bertambah beban maka rasio peningkatan tegangan air pori di bawah beban cenderung semakin berkurang. Rasio peningkatan tegangan air pori maksimum tertinggi didapat pada pengujian tanpa beban dengan percepatan maksimum gempa 0,4g sebesar 1,338 sampai 1,457 dan terendah pada beban 0,46 t/m2 dengan percepatan gempa 0,3g. Secara keseluruhan potensi likuifaksi berkurang pada saat beban lebih dari 0,22 t/m2 dan pada saat beban maksimum 0,46 t/m2, potensi likuifaksi mengalami penurunan antara 41,90% - 53,10%. Percepatan gempa yang besar menghasilkan rasio peningkatan tegangan air pori lebih tinggi dan durasi terjadinya likuifaksi lebih lama. Durasi likuifaksi antara 43 sampai 54 detik. Penurunan terbesar terjadi pada pengujian tanpa beban dan percepatan gempa 0,4g sebesar 4 cm sedangkan penurunan terendah terjadi pada pengujian dengan beban 0,46 t/m2 dan percepatan gempa 0,3g sebesar 0,53 cm. Kata Kunci : Likuifaksi, meja getar, beban, rasio peningkatan tegangan air pori xvii ABSTRACT One of the structural failure of soil caused by the earthquake is liquefaction. Liquefaction occurs in the layer of water-saturated loose sand due to receiving cyclic loading of earthquake vibrations that changes the nature of soil from solid to liquid state so that thes soil is unable to sustain the load of the building on or above it. To determine the effect of the load on the liquefaction potential experimental test was performed. An experimental study using a shaking table was performed using sample of sand which is from the sand of Kali Opak Pleret Yogyakarta. Earthquake parameters considered in this study include the earthquake maximum acceleration of 0,3g, 0,35g, 0,4g with duration of vibrating was for 32 seconds. Testing was done without load and load increase of 0,15 t/m2, 0,31 t/m2 and 0,46 t/m2. The value of relative density sand in the test ranged from 25 – 27 % accordance with the relative density in the field. Tool pore water pressure readings used in this study are pressure transducer and headmeter. Results evaluation of testing was done by comparing the pore water pressure and effective stress. Liquefaction would occur if the ratio of the increase in pore water pressure is more than one or equal to one (ru ≥ 1) otherwise if ru < 1 liquefaction would not occur. Based on the results of sieve analysis testing, sand of Kali Opak Pleret belongs to the zone of most susceptible to liquefaction. The same evident is shown from the observation with a stereo microscope, the shape of the sand particles tends to look round and almost uniformly, so it is liquefaction potential. Result testing using shaking table showed that the more is the load increase, the less is ratio of pore water pressure increase under the load. The highest ratio of the increase in maximum pore water pressure was obtained at testin without load with earthquake maximum acceleration of 0,4g is as much as 1,338 (pressure transducer I), 1,457 (pressure transducer II), and 1,379 (headmeter) and the lowest one is at the load of 0,46 t/m2 with earthquake acceleration of 0,3g. Over all potential liquefaction defence at load more than 0,22 t/m2 and at maximum load 0,46 t/m2, potential liquefaction suffering decrease between 41,90% - 53,10%. The high earthquake acceleration generates the higher ratio of increase of pore water preasure and the longer duration of liquefaction occurence. The maximum duration of liquefaction is 54 seconds (pressure transducer I), 43 seconds (pressure transducer II), 46 seconds (headmeter). The largest decrease occurred in the testing without load and earthquake acceleration of 0,4g is 4 cm while the smallest one occurred in the testing with a load of 0,46 t/m2 and earthquake acceleration of 0,3 g is 0,53 cm. Keywords: Liquefaction, shaking table, load, increase ratio of pore water pressure xviii