abstrak aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase beberapa tumbuhan
advertisement

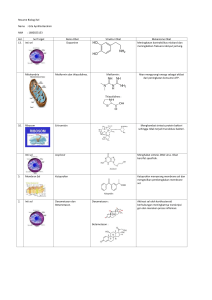
ABSTRAK AKTIVITAS INHIBITOR TOPOISOMERASE BEBERAPA TUMBUHAN INDONESIA ANGGOTA SUKU APOCYNACEAE, SIMAROUBACEAE, DAN MAGNOLIACEAE DENGAN METODE MECHANISM-BASED YEAST BIOASSAY SERTA ISOLASI SENYAWA AKTIF TUMBUHAN TERPILIH Oleh: Ade Zuhrotun NIM 30712005 (Program Studi Doktor Farmasi) Penyakit kanker ditandai dengan pertumbuhan sel tidak terkendali dan penyebarannya melalui sistem limfatik dan pembuluh darah menuju jaringan atau bagian tubuh lainnya. Pertumbuhan sel ini akan terus berlangsung dan menyebabkan kerusakan organ-organ vital manusia bahkan kematian. Jumlah kasus kanker di dunia mengalami peningkatan dari 12,7 juta pada tahun 2008 menjadi 14,1 juta pada tahun 2012. Angka ini diperkirakan akan meningkat menjadi 25 juta pada kurun waktu dua dekade. Sementara di Indonesia, prevalensi kanker pada tahun 2013 yaitu 1,4 ‰ atau sekitar 347.792 orang. Kombinasi operasi, radiasi dan kemoterapi merupakan pilihan yang sering dilakukan untuk mengobati kanker. Beragamnya tipe sel kanker pada tiap pasien, stadium panyakit, adanya resiko toksisitas obat, efek samping dan resistensi dalam kemoterapi membuat kanker sulit diobati. Hal ini menjadi tantangan dan motivasi untuk mencari sumber baru obat antikanker. Saat ini, sebanyak 74 dari 488 obat antikanker yang diluncurkan National Cancer Institute (NCI) Amerika Serikat merupakan obat asal tumbuhan. Sementara di Indonesia, sebanyak 16 dari 74 obat antikanker yang beredar merupakan obat asal tumbuhan. Menurut NCI, ada Families of Special Interest (FOSI) atau beberapa suku tumbuhan yang diperkirakan memiliki aktivitas antikanker, diantaranya yaitu Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae dan Magnoliaceae. Di Indonesia, tercatat sekitar 63 jenis tumbuhan Apocynaceae, 11 jenis tumbuhan Simaroubaceae dan 18 jenis tumbuhan Magnoliaceae yang tersebar di berbagai wilayah. Salah satu metode uji in vitro yang bisa digunakan dalam rangka mencari antikanker dari bahan alam yaitu mechanism-based yeast bioassay. Hasil pengujian ini berkorelasi terhadap salah satu mekanisme kerja senyawa antikanker yaitu inhibitor enzim topoisomerase. Sampai saat ini belum pernah dilaporkan adanya aktivitas inhibitor enzim topoisomerase terhadap tumbuhan Indonesia dari suku Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae dan Magnoliaceae. Oleh karena itu, penelitian ini dilakukan untuk penapisan aktivitas inhibitor enzim topoisomerase beberapa i tumbuhan Indonesia anggota suku tersebut dan isolasi senyawa aktif tumbuhan terpilih. Penapisan aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase dilakukan terhadap ekstrak metanol kulit batang 15 jenis tumbuhan suku Apocynaceae, 3 jenis tumbuhan suku Simaroubaceae dan 2 jenis tumbuhan suku Magnoliaceae dengan metode mechanism-based yeast bioassay terhadap S. cerevisiae galur mutan (DNA repairatau recombination deficient). Hasilnya menunjukkan bahwa ekstrak Kibatalia arborea (Blume) G. Don. dan Michelia champaca L. memiliki aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase I dan II. Ekstrak Plumeria alba L., Tabernaemontana macrocarpa Jack., Wrightia pubescens Blume, Picrasma javanica Blume, Picrodendron baccatum Krug. & Urb. Ex. Urb., dan Quassia indica L. Nooteboom memiliki aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase I. Sedangkan ekstrak Ochrosia citrodora Lauterb & K. Schum dan Michelia alba DC. memiliki aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase II. Berdasarkan hasil penapisan, ekstrak Michelia champaca L. dipilih sebagai ekstrak terbaik yang menunjukkan aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase I dan II. Ekstrak tersebut memiliki efek toksik berdasarkan metode brine shrimp lethality bioassay (LC50<1000 g/mL) dan memiliki aktivitas antijamur. Data ini menunjukkan bahwa tumbuhan ini memiliki potensi sebagai antikanker. Oleh karena itu, M.hampaca dijadikan tumbuhan terpilih untuk dilakukan isolasi senyawa aktif. Ekstrak metanol M. champaca difraksinasi dengan metode ekstraksi cair-cair (ECC). Berdasarkan hasil uji aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase dengan mechanism-based yeast bioassay dan KLT bioautografi, diketahui bahwa senyawa target yaitu bercak ke-5 (Rf 0,68) dalam fraksi etil asetat dengan pengembang campuran kloroform-metanol (9:1). Fraksi etil asetat dipisahkan lebih lanjut dengan gabungan metode kromatografi cair vakum dan kromatografi kolom klasik. Pada tahap akhir dilakukan pemurnian senyawa dengan cara rekristalisasi menggunakan pelarut kloroform. Hasil isolasi berupa kristal jarum berwarna kuning dengan jarak lebur 271,5-272,6 C, yang dinamakan isolat MCET51. Uji aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase isolat MCET51 dilakukan dengan metode mechanism-based yeast bioassay dan reaksi enzimatik terhadap human topoisomerase I. Hasilnya menunjukkan bahwa isolat aktif sebagai inhibitor topoisomerase I dan II. Karakterisasi isolat MCET51 telah dilakukan dengan spektrofotometri UV-Vis, spektrofotometri Inframerah, spektrometri massa dan spektrometri resonansi magnet inti proton (1H), karbon (13C), Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence (HSQC) serta Heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation spectroscopy (HMBC). Berdasarkan data karakterisasi dan setelah dibandingkan dengan pustaka, disimpulkan bahwa isolat MCET51 adalah liriodenin. Aktivitas ekstrak M. champaca dan liriodenin sebagai inhibitor topoisomerase I dan II dengan metode mechanism-based yeast bioassay untuk pertama kali ii dilaporkan pada penelitian ini. Selain itu, aktivitas liriodenin sebagai inhibitor topoisomerase I dengan metode enzimatik terhadap human topoisomerase I untuk pertama kali dilaporkan pada penelitian ini. Penelitian lainnya hanya melaporkan liriodenin sebagai inhibitor topoisomerase II. Hasil penelitian ini sejalan dengan laporan NCI yang menyebutkan bahwa suku Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae dan Magnoliaceae termasuk ke dalam FOSI atau suku tumbuhan yang diperkirakan mengandung zat aktif antikanker. Senyawa yang diisolasi dari tumbuhan terpilih Michelia champaca L., yaitu liriodenin memiliki aktivitas inhibitor topoisomerase I dan II yang merupakan salah satu mekanisme obat-obat antikanker. Kata kunci: Inhibitor topoisomerase, mechanism-based yeast bioassay, Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae, Magnoliaceae, Michelia champaca L. iii ABSTRACT TOPOISOMERASE INHIBITIONS ACTIVITY OF SEVERAL INDONESIAN PLANTS OF APOCYNACEAE, SIMAROUBACEAE, MAGNOLIACEAE USING MECHANISM-BASED YEAST BIOASSAY AND ACTIVE COMPOUND ISOLATION OF SELECTED PLANT By: Ade Zuhrotun NIM 30712005 (Doctoral Study Program of Pharmacy) Cancers is characterized by unregulated growth and spread of cells through lymphatic system and bloodstream to other parts of the body. These cells growth will continue and damage vital organs or eventually death. In the world wide, cancer incidences increases from 12.7 million in 2008 to 14.1 million in 2012 and it was predicted to be 25 million over the next two decades. In Indonesia, cancer prevalence in 2013 was 1.4 ‰ or 347,792 people. Combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are the most chosen therapy for cancer. Variation of cancer type for each patient, diseases stadium, toxicity risks, side effects and drug resistances made cancer treatments often difficult. So these conditions become opportunities and motivated the research for new anticancer agents. Recently, 74 of 488 anticancer drugs that are released by National Cancer Institute (NCI) of USA derived from plants. Whereas in Indonesia 16 of 74 anticancer drugs that are currently used derived from plants. The NCI has reported Families of Special Interest (FOSI) or plant families that are active as anticancer or contain anticancer agents, such as Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae and Magnoliaceae. In Indonesia, about 63 species of Apocynaceae, 11 species of Simaroubaceae and 18 species of Magnoliaceae are grown and distributed in many areas. Mechanism-based yeast bioassay is one of the in vitro assay that is used to search anticancer agents from natural products. This assay’s result had correlation to a mechanism of anticancer agents i.e topoisomerase enzyme inhibitor. Activity of this inhibitor of Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae and Magnoliaceae has not been reported yet, so this research was aimed to screen some Indonesian plants of those families and further to isolate active compound of selected plant. Screening activity was tested on methanol bark extract of 15 species of Apocynaceae, 3 species of Simaroubaceae and 2 species of Magnoliaceae against S. cerevisiae mutant (DNA repair- or recombination deficient). The results showed that extract of Kibatalia arborea (Blume) G. Don. and Michelia champaca L. were active as topoisomerase I and II inhibitors. Extract of Plumeria alba L., Tabernaemontana macrocarpa Jack., Wrightia pubescens Blume., i Picrasma javanica Blume., Picrodendron baccatum Krug. & Urb. Ex. Urb., and Quassia indica (L) Nooteboom were active as topoisomerase I inhibitors, while extract of Ochrosia citrodora Lauterb & K. Schum and Michelia alba DC. were active as topoisomerase II inhibitors. Based on the screening, M. champaca extract was selected as the best choice that showed as topoisomerase I and II inhibitors. It had toxic effect based on brine shrimp lethality bioassay (LC50<1000 g/mL) and was activity as antifungi. Those data showed that the plant had potential active as anticancer agent. So, the plant was selected for its active compound isolation. The extract of M. champaca was fractionated by liquid-liquid extraction (LLE). Based on activity test results of topoisomerase inhibitor, using mechanism-based yeast bioassay and bioautography TLC, showed that the target compound from the fraction was spot number 5 (Rf 0.68) with chloroform-methanol (9:1) as development system. The ethyl acetate fraction was further separated by combination of fast column chromatography, followed by classical column chromatography. At the end, purification process was done by recrystallization using chloroform. The yellow needles crystal with melting point of 271.5-272.6 C, was named as MCET51 isolate. Topoisomerase inhibitor activity of MCET51 then was also tested by mechanismbased yeast bioassay methods and enzymatic reaction to human topoisomerase I. The result showed that the isolate was active as topoisomerase I and II inhibitors. Characterization of MCET51 was done by UV-Vis, infrared spectrophotometric, mass spectrometric and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proton (1H), carbon (13C), Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence (HSQC) and Heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation spectroscopy (HMBC) methods. Based on characterization data compared to literatures, it can be concluded that MCET51 was liriodenine (C17H9NO3). The activity of M. champaca extract and liriodenine as topoisomerase I and II inhibitors using mechanism-based yeast bioassay were the first time reported by this research. And the activity of liriodenine as topoisomerase I inhibitor using enzymatic reaction to human topoisomerase I was the first time reported by this research, whereas other research only reported liriodenin as topoisomerase II inhibitor by different methods. The results of this research was in line with NCI, that reported Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae and Magnoliaceae as FOSI or plant families that contained anticancer agents. Isolated compound from selected plant Michelia champaca L., i.e liriodenine was proven as topoisomerase I and II inhibitors. These results can be used as scientific evidence for further research to develop Indonesian plant as herbal anticancer. Keywords: Topoisomerase inhibitor, mechanism-based yeast bioassay, Apocynaceae, Simaroubaceae, Magnoliaceae, Michelia champaca L. ii