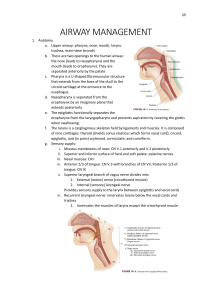
Ensure adequacy of the airway Confirm adequacy of ventilation Define “definitive airway” Maintain adequate oxygenation in all phases of airway management How do I know the airway is adequate? How do I know ventilation is adequate? How do I know oxygenation is adequate? What are the pitfalls? …talks clearly? …is hoarse? …cannot respond? …is intubated? Airway is adequate Management: Observation and selective intubation High index of concern with • Maxillofacial injury • Soft-tissue injury of neck • Facial or neck burns Laryngeal injury Laryngeal / tracheal burn Management: Evaluate and perform • Careful endoscopic exam • Careful and gentle intubation, or • Surgical airway? GCS Score<9 Obstruction due to • Tongue • Aspiration • Foreign body • Maxillofacial injury • Neck injury Cyanosis Rocking respirations Decreased or no air exchange Face or neck crepitus Neck hematoma or swelling Simple management maneuvers • Suction • Chin lift • Jaw thrust “Definitive airway:” Cuffed tube in trachea Assess for sign of obstruction Confirm correct ET tube position Auscultate in medial axillae Assess oxygenation (pulse oximeter) Assess ventilation (CO2 detector) Obtain chest x-ray Protect the cervical spine during airway management ! What do I see? What do I feel? What do I hear? What do I measure? What might I find? How do I manage the patient? Respiratory rate and effort Respiratory distress / labored Cyanosis Restlessness / anxiety Chest asymmetry / paradoxical breathing Crepitance Local tenderness Asymmetric respiratory excursion Noisy breathing Asymmetric breath sounds Absent breath sounds Mental status Vital signs Pulse oximetry End-tidal CO2 ABGs Tension pneumothorax Pneumothorax Hemopneumothorax Malpositioned ET tube Neurologic deficit Direct neck /chest injury Establish an appropriate airway Administer supplemental oxygen Decompress the chest Reposition the ET tube Provide mechanical ventilation Perform a surgical airway Mental status evaluation Vital signs Pulse oximetry ABGs Airway versus ventilation RSI— Inability to intubate Dislodged / malpositioned ET tube Aspiration Equipment failure How do I know the airway is adequate? How do I know ventilation is adequate? How do I know oxygenation is adequate? What are the pitfalls?