bahasa pemrograman - E
advertisement

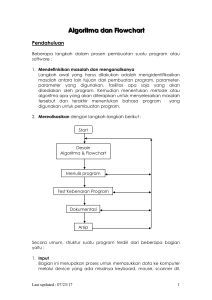
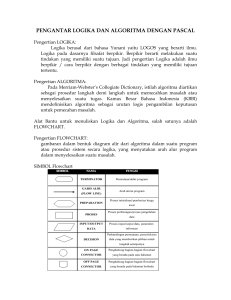
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE :: BAHASA PEMROGRAMAN :: USING JAVA Tentang saya • • • • • • Nur Cahyo Wibowo, S.Kom, M.Kom S1 Teknik Informatika ITS 1998 – 2003 S2 Teknik Informatika ITS 2006 – 2009 HP 081 230 544 039 Griya Pesona Asri E-21, Medokan Ayu Email: [email protected] atau [email protected] (YM) • Face book : Nur Cahyo Wibowo • MK : BP, BP2, Struktur Data • http://bluejundi.wordpress.com BAHASA PEMROGRAMAN • PENILAIAN: – UTS/UAS – TUGAS/QUIZ – KEHADIRAN 60 % 30 % 10 % • NILAI AKHIR = (NA UTS + NA UAS) / 2 INTRO TO PROGRAMMING PROLOG: THE COMPUTER SYSTEM SOFTWARE HARDWARE PROGRAMMING O/ S GAMES APPLICATIONS BRAINWARE PROGRAMMING FRAMEWORK FILE APLIKASI COMPILING RUNNING SOURCE CODE MEMORI/ RAM OPERATING CODING USER PROGRAMMER PROGRAMMING HISTORY LANGUAGE GENERATION • 1ST GENERATION – Machine Language ASSEMBLER • 2ND GENERATION – Human Language FORTRAN, C, PASCAL, BASIC • 3RD GENERATION – Visual, OOP DELPHI, JAVA, VISUAL BASIC • 4TH GENERATION – DBMS SQL (STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE) ALGORITHM & FLOWCHART • Tujuan : 1. Mahasiswa dapat menjelaskan apa itu algoritma dan flowchart. 2. Mahasiswa dapat menyebutkan beberapa simbol dasar flowchart. 3. Mahasiswa terampil dalam membuat algoritma dan flowchart untuk suatu studi kasus. Lee & Lu Algorithm is… • A computable set of steps to achieve a desired • • • result. Paul E. Black An explicit, precise, unambiguous, mechanicallyexecutable sequence of elementary instructions. Jeff Erickson An effective method for solving a problem using a finite sequence of instructions. Wikipedia A list of well-defined instructions for completing a task. Wikipedia ALGORITHM • Adalah urutan langkah-langkah logika yang • 1. 2. 3. menyatakan suatu tugas dalam menyelesaikan suatu masalah atau problem. Contoh: Buat algoritma untuk menentukan apakah suatu bilangan merupakan bilangan ganjil atau bilangan genap. Algoritmanya : Bagi bilangan dengan bilangan 2. Hitung sisa hasil bagi pada langkah 1. Bila sisa hasil bagi sama dengan 0 maka bilangan itu adalah bilangan genap tetapi bila sisa hasil bagi sama dengan 1 maka bilangan itu adalah bilangan ganjil. Some Example Buatlah algoritma untuk: 1. Membuat mi instan 2. Sarapan 3. Berangkat ke kampus 4. Menyalakan komputer 5. Mencetak file dokumen Note: definisikan terlebih dulu kondisi awal dan akhir 1. 2. 3. 4. Buka file dokumen Cek printer Jika lampu menyala klik tombol printer Jika lampu tidak menyala maka ulangi langkah 2. What is Flowchart • A diagram that uses graphic symbols to depict • the nature and flow of the steps in a process. Another name for this tool is flow diagram. Maps or graphical representations of a process. Steps in a process are shown with symbolic shapes, and the flow of the process is indicated with arrows connecting the symbols. What Flowchart for • Promote process understanding by explaining • the steps pictorially. People may have differing ideas about how a process works. A flowchart can help you gain agreement about the sequence of steps. Flowcharts promote understanding in a way that written procedures cannot do. One good flowchart can replace pages of words. Flowchart & Programming • The flowchart is a means of visually presenting the flow • • • of data through an information processing systems, the operations performed within the system and the sequence in which they are performed. Program flowchart, which describes what operations (and in what sequence) are required to solve a given problem. The program flowchart can be likened to the blueprint of a building. As we know a designer draws a blueprint before starting construction on a building. Similarly, a programmer prefers to draw a flowchart prior to writing a computer program. MEANING OF A FLOWCHART • Flowcharts are generally drawn in the early stages of • • • • • formulating computer solutions. Flowcharts facilitate communication between programmers and business people. These flowcharts play a vital role in the programming of a problem and are quite helpful in understanding the logic of complicated and lengthy problems. Once the flowchart is drawn, it becomes easy to write the program in any high level language. Often we see how flowcharts are helpful in explaining the program to others. Hence, it is correct to say that a flowchart is a must for the better documentation of a complex program. FLOWCHART • Biasa disebut dengan diagram alir. • Salah satu metode untuk merepresentasikan algoritma selain pseudocode dan urut-urutan langkah. • Menggunakan simbol-simbol bangun datar beserta anak panah sebagai penunjuk arah proses. Some Guidelines 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. The flowchart should be clear, neat and easy to follow. There should not be any room for ambiguity. The usual flow direction is from left to right or top to bottom. Only one flow line should come out from a process symbol. Only one flow line should enter a decision symbol, but two or three flow lines should leave the decision symbol. Only one flow line is used in conjunction with terminal symbol. Write within standard symbols briefly. As necessary, you can use the annotation symbol to describe more clearly. If the flowchart becomes complex, it is better to use connector symbols to reduce the number of flow lines. Avoid the intersection of flow lines. Ensure that the flowchart has a logical start and finish. It is useful to test the validity of the flowchart by passing through it with a simple test data. SIMBOL NAMA FUNGSI TERMINATOR Permulaan/ akhir program GARIS ALIR (FLOW LINE) Arah aliran program PREPARATION Proses inisialisasi/ pemberian harga awal PROSES Proses perhitungan/ proses pengolahan data INPUT/ OUTPUT DATA Proses input/ output data, parameter, informasi PREDEFINED PROCESS (SUB PROGRAM) Permulaan sub program/ proses menjalankan sub program DECISION Perbandingan pernyataan, penyeleksian data yang memberikan pilihan untuk langkah selanjutnya ON PAGE CONNECTOR Penghubung bagian-bagian flowchart yang berada pada satu halaman OFF PAGE CONNECTOR Penghubung bagian-bagian flowchart yang berada pada halaman berbeda Contoh: Flowchart untuk menentukan bilangan genap atau ganjil Start Input Bilangan Hitung sisa bagi antara bilangan dengan angka 2 A Apakah Sisa = 0 T Y Cetak Genap A End Cetak Ganjil AKAR PERS. KUADRAT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Mulai Masukkan nilai variabel A, B, C Hitung D = B2 – 4*A*C Jika D = 0 maka X1 = X2 = – B/(2*A) Tapi jika D < 0 maka X1, X2 Imaginer selain itu maka X1,2 = (– B ± √D)/(2*A) Tampilkan X1, X2 Selesai DIKET: Y = AX2 + BX + C Start Input Nilai A, B, C FLOWCHART AKAR PERSAMAAN KUADRAT D = B2 – 4*A*C Y D=0 ? T X1 = X2 = – B/(2*A) Y D<0 ? X = (– B ± √D)/(2*A) T X1, X2 Imaginer Cetak X1, X2 End Bilangan Faktorial 1. Mulai 2. Masukkan N (N adalah bilangan yang akan 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. dihitung nilai faktorialnya) Set variabel Faktorial 1 Set variabel Angka 1 Hitung Faktorial Faktorial * Angka Angka Angka + 1 Apakah Angka > N ? Jika TIDAK kembali ke langkah (5). Jika YA tampilkan nilai Faktorial. Selesai FLOWCHART FAKTORIAL EX. 4! = 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 24 Start Input N A Faktorial = Faktorial * Angka Angka = Angka + 1 T Faktorial 1 Angka 1 Angka > N ? Y A Cetak Faktorial End LATIHAN SOAL 1. Buatlah flowchart untuk memasak mi instan! 2. Buatlah flowchart untuk naik angkot/ lyn! 3. Buat algoritma untuk menghitung jumlah N suku dari 4. 5. 6. deret aritmatika dengan pola berikut : Sn = 3 + 7 + 11 + …… + (4n-1) Buat flowchart untuk mencetak pasangan nilai X dan Y dimana hubungan antara X dan Y memenuhi persamaan Y = X3 – 2X +1 dan nilai x berubah dari –10 sampai 10 ! Buat algoritma + flowchart untuk menentukan apakah suatu bilangan merupakan bilangan prima atau bukan! Buat algoritma + flowchart untuk mencetak N buah bilangan prima yang pertama!