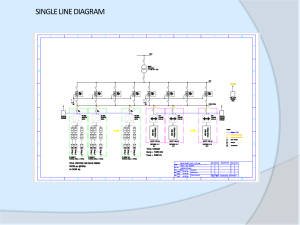
Trixie Marsya Rofifah 04211841000042 FLYBALL GOVERNOR The Centrifugal Governor or Flyball Governor was invented by James Watt. What is flyball governor? A flyball governor is a specific type of governor with a feedback system that controls the speed of an engine by regulating the flow of fuel or working fluid, so as to maintain a near-constant speed. Flyball governer uses the principle of proportional control. Flyball governer composed by two balls of equal mass, which are attached to the arms as shown in Figure. These balls are known as fly balls. The balls revolve with a spindle, which is driven by the engine through bevel gears. Figure 1 The upper ends of the arms are pivoted to the spindle, so that the balls may rise up or fall down as they revolve about the vertical axis. The arms are connected by the links to a sleeve, which is keyed to the spindle. This sleeve revolves with the spindle, but can slide up or down. The balls and the sleeve rises when the spindle speed increases, and falls when the speed decreases. In order to limit the travel of the sleeve in upward and downward directions, two stops, S are provided on the spindle. The sleeve is connected by a bell crank lever to a throttle valve. The supply of the working fluid decreases when the sleeve rises and increases when it falls. The centrifugal governor has various components inside it that allow it to keep the speed of an engine stable, below are the parts of the centrifugal governor. Figure 2 The parts shown in the image are as follows – The sliding collar: this can move up and down on the main shaft 3 bearings: these allow the gold parts to open in a scissor-like motion main shaft: this is the main shaft upon which everything else rests idle speed plate:this stops the engine going to slow, if this plate was not here the centrifugal governor could cut the fuel supply off from the engine weighted balls: these rise under centrifugal motion as the whole system begins to rotate Pulley to engine: there is a belt attached to this pulley which goes directly to the engine, therefore when the engine speeds up or slows down, the centrifugal governor follows suit Other than that, flyball governor has pivot as the controller, steam as the plant, flyball as the censor, butterfly valve as the actuator. The input and the output of this control system is control how much speed that the engine needs. The governor can move in two directions, rotary motion and up and down Figure 3 So, as we can see, Flyball Governor is a really simple and useful to increase the efficiency and efficient on Steam Engine. It is really important to helps our lives because this type of governor is needed for many kind of industries such as textile, tableware, coal mining, steel mills, etc. These kind of industries required a stable engine speed from their steam engines to run effectively and efficiently. As soon as this governor was introduced it was received by all industries. In fact it has been used ever since, it can still be found in modern car engines, jet engines and many other rotating machines. This kind of governor very useful too in maritime industries. On modern propellers, the centrifugal governors senses shaft RPM and adjusts the pitch of the blade to vary the torque load on the engine. Sources https://www.cds.caltech.edu/~murray/courses/cds101/fa03/caltech/am03_ch1-27sep03.pdf https://www.physics.wisc.edu/ingersollmuseum/exhibits/mechanics/CentrifugalGovernor http://www.epicphysics.com/engineering/centrifugal-governor/ https://www.irjet.net/archives/V4/i1/IRJET-V4I1185.pdf Trixie Marsya Rofifah 0421184100042 ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR A governor, or speed limiter, is a device used to measure and regulate the speed of a machine, such as an engine. Governor divided by two types, mechanical governor and electronic governor. An Electronic governor provides engine speed adjustment from no-load condition to full load. Earlier, mechanical governors were used, but with the advancement of electronic components, the control features of governors have become much more flexible and this type of governor more used for speed control. Figure 1 Electronic governor senses this engine speed and converts into electrical pulses or frequency and sends it to electronic control unit. Electronic control unit senses these pulses or frequencies and controls the actuator which in turn controls the fuel injecting pump. Thus at various loads or speeds the electronic governor works efficiently. These governors typically are retrofitted to applications that now require a governor. They pick up the engine speed from the flywheel ring gear’s teeth and control it electronically. If the engine is running at some intermediate speed between idling and maximum, but at less than full load, any change in load will cause a speed change. Electronic governor senses this engine speed and converts into electrical pulses or frequency and sends it to electronic control unit. Electronic control unit senses these pulses or frequencies and controls the actuator which in turn controls the fuel injecting pump. Thus at various loads or speeds the electronic governor works efficiently. Figure 2 The electronic controller has different modes of operation to implement various functions. These include: 1. Detecting the starting of an engine and subsequently directing the fuel supply. 2. Suppressing the smoke generated by the engine as its speed increases. 3. Adjusting the droop percentage. A detailed explanation of the droop percentage is given below. 4. Remote speed control. 5. Idle speed operation: It provides fixed speed control over the entire torque capacity of the engine. 6. Maximum speed control: It is used to eliminate over speeding of the engine Figure 3 What are the components of electronic governor control system? From figure above, we know that electronic governor has governor as controller, fuel valves as actuator, magnetic pickup unit as censor, and plant as fuel. The input and the output of this control system is control how much speed that the engine needs. So, from explanation above, we know that electronical governore is more flexible and modern than mechanical governor. Generally, electronic systems are not as reliable as mechanical systems. But it is possible to build reliable control systems with more complex operations, accuracy, precision and reliability. It can deliver fast, no-droop response to load changes and isochronous speed control for gensets. They are up to 200 times faster than mechanical governors. This means that there is no droop on gen-sets, so power stays constant under variable loads on pumps and other engine applications. Sources https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326675017_Design_of_an_Electronic_Governor_for_a_ Diesel_Generator_with_Synchronous_Isochronous_and_Islanded_Modes https://www.ijraset.com/fileserve.php?FID=3286 https://www.ipu.co.uk/products/electronic-governors/ https://www.marineinsight.com/tech/types-of-governors-for-engines-used-on-ships/ Trixie Marsya Rofifah 04211841000042 DEEP HOLE DRILLING SYSTEM A deep hole is defined by its depth-to-diameter ratio (D:d), and typically holes greater than 10:1 are considered deep holes. Deep hole drilling has a range of applications across several industries, with its origins tracing back to the need for straighter, more accurate gun barrels, and expanding as other industries integrated deep hole drilling processes to improve their own applications. In maritime field especially offshore, deep hole drilling system can be used in deepwater drilling. Deepwater drilling, or Deep well drilling,is the process of creating holes by drilling rig for oil mining in deep sea. There are approximately 3400 deepwater wells in the Gulf of Mexico with depths greater than 150 meters. Figure 1 Figure 2 Another deep hole drilling system application in maritime field is shipbuilding. In the manufacture of ships rotor shafts in particular but also in the case of numerous components for pumps and powertrains, the field of shipbuilding involves challenging deep hole drilling tasks that can be done with great precision, reliably, and efficiently with deep hole drilling machines. But, this paper will talk about deep hole drilling system application in offshore drilling. How does deep hole drilling works in deep water? As the drill pipes are connected, the conductor pipe and guide are run down to the sea floor. After the conductor pipe penetrates the sea floor the drill pipe is released and pulled back to the vessel. A large drill bit connected to the bottom of the drill pipe is run down to the sea floor. The drill bit is lead down to the bottom of the hole through the conductor pipe. The drill bit rotates and drills the sediment and rock below the sea bed. Sea water is sprayed from nuzzles on the drill bit to raise the cuttings to the sea floor. After drilling several hundred meters the drill bit is pulled back to the vessel. A casing pipe about 50cm in diameter is set into the drill hole to keep it from collapsing. The casing pipe is run down through the conductor pipe and is inserted into the hole using the drill pipe. Figure 3 Figure 4 The main components of offshore deep hole drilling are: Crown block: sheaves (pulleys) over which the wire ropes attached to the traveling block pass. Travelling block: used to support the weight of the drill string and to hoist drill pipe into and out of the hole. Monkey board: small platform from which a monkey (derrick man) can manoeuvre pipe stands into and out of the finger board. Finger board: provides a location for the drill pipe stands. Draw-works: it is a large hydraulically or electrically driven winch which provides motive power to operate the travelling block and the rotary table. Rotary table: it imparts rotary motion to the drill string and permits the passage of the drill string through bushings and also rotates the Kelly, which is a hollow square pipe that fits into the top section of a drill pipe and provides it with both rotational motion and drilling mud. Mousehole: a pipe into the drill floor in which a new section of drill pipe is inserted before connecting it to the Kelly and including it in the drill string. Rathole: a pipe into the drill floor for the Kelly to go through while making a trip. Pipe rack: area of deck in front of drilling derrick to store drill pipe and casing. “V” door: V shaped opening in the windwall between the pipe rack and the drill floor. Cat line: small winch used to transport drill pipe and casing from pipe rack to drillfloor. Drill pipe: it is supplied in 30 ft (9m) lengths of either 3.5 or 5 inch diameter with pin and box couplings at each end to permit assembly and disassembly of the drill pipe. swivel - large handle that holds the weight of the drill string; allows the string to rotate and makes a pressure-tight seal on the hole kelly - four- or six-sided pipe that transfers rotary motion to the turntable and drill string turntable or rotary table - drives the rotating motion using power from electric motors drill bit(s) - end of the drill that actually cuts up the rock; comes in many shapes and materials (tungsten carbide steel, diamond) that are specialized for various drilling tasks and rock formations For the component of control system, offshore deep hole drilling has hole depth sensor for sensors for tracking how depth of the well we drill, draw works as the controller, drill bit as a plant, and swivel as the actuator. The input/output is amount of the depth of the hole. In the years that followed, petroleum companies moved even farther into the ocean. Today's oil rigs are truly gigantic structures. Some are basically floating cities, employing and housing hundreds of people. Other massive production facilities sit atop undersea towers that descend as far as 4,000 feet (1,219 meters) into the depths -- taller than the world's most ambitious skyscrapers. In an effort to sustain their fossil fuel dependency, humans have built some of the largest floating structures on Earth. We can conclude that deep hole drilling control system is very useful and important for maritime fields especially in offshore drilling system. Sources Leheta, HW. Offshore Drilling. Egypt: University of Alexandria http://www.drillingformulas.com/how-does-deep-water-drilling-work/ https://www.arab-oil-naturalgas.com/ http://www.diamondoffshore.com/offshore-drilling-basics https://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/energy/offshore-drilling.htm