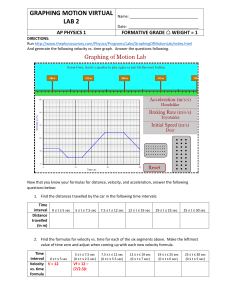
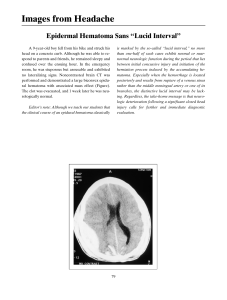
https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is First Degree Heart Block. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is normal. The PR interval is prolonged (>0.20 sec). The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). A first degree AV block occurs when electrical impulses moving through the Atrioventricular (AV) node are delayed (but not blocked). First degree indicates slowed conduction without missed beats.. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Premature Junctional Complex. Look for rhythm that is regular with premature beats, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is present before, during (hidden) or after qrs, if visible it is inverted. The PR interval is absent or short. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Atrial Flutter. Look for rhythm that is regular or irregular, with heart rate that is fast (250-350 bpm) for atrial, but ventricular rate is often slower. Notice that the P wave is not observable, but saw-toothed flutter waves are present. The PR interval is not measureable. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). That's correct! This tracing is Premature Ventricular Complex. Look for rhythm that is irregular, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is absent. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically wide (> 0.10 sec), bizarre appearance. Two PVCs together are termed a couplet while three PVCs in a row with a fast rhythm is ventricular tachycardia. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Atrial Flutter. Look for rhythm that is regular or irregular, with heart rate that is fast (250-350 bpm) for atrial, but ventricular rate is often slower. Notice that the P wave is not observable, but saw-toothed flutter waves are present. The PR interval is not measureable. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Second Degree Heart Block Type II. Look for rhythm that is regular (atrial) and irregular (ventricular), with heart rate that is characterized by atrial rate usually faster than ventricular rate (usually slow). Notice that the P wave is normal form, but more p waves than qrs complexes. The PR interval is normal or prolonged. The QRS is typically normal or wide. This tracing is Second Degree Heart Block Type I. Look for rhythm that is irregular but with progressively longer pr interval lengthening, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is normal. The PR interval is progressively longer until a qrs complex is missed, then cycle repeats. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Ventricular Tachycardia. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is fast (100-250 bpm). Notice that the P wave is absent. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically wide (>0.10 sec), bizarre appearance. Muscle tremor noise is present in this tracing. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill This tracing is Second Degree Heart Block Type I. Look for rhythm that is irregular but with progressively longer pr interval lengthening, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is normal. The PR interval is progressively longer until a qrs complex is missed, then cycle repeats. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). That's correct! This tracing is Ventricular Fibrillation. Look for rhythm that is highly irregular, with heart rate that is unmeasurable. Notice that the P wave is absent. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically none. EKG tracings is a wavy line. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill This tracing is Third Degree Heart Block. Look for rhythm that is regular, but atrial and ventricular rhythms are independent, with heart rate that is characterized by atrial rate usually normal and faster than ventricular rate. Notice that the P wave is normal shape and size, may appear within qrs complexes. The PR interval is absent: the atria and ventricles beat independently.. The QRS is typically normal, but wide if junctional escape focus. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Pacemaker Single Chamber Ventricular. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is First Degree Heart Block. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is normal. The PR interval is prolonged (>0.20 sec). The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). A first degree AV block occurs when electrical impulses moving through the Atrioventricular (AV) node are delayed (but not blocked). First degree indicates slowed conduction without missed beats.. That's correct! This tracing is Bundle Branch Block. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is normal. The PR interval is normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS is typically wide (>0.12 sec). https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Accelerated Junctional Rhythm. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is normal (60-100 bpm). Notice that the P wave is present before, during (hidden) or after qrs, if visible it is inverted. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Supraventricular Tachycardia. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is fast (150-250 bpm). Notice that the P wave is merged with t wave. The PR interval is normal (0.12 sec). The QRS is typically normal (.10 sec). PR interval can be difficult to measure. That's correct! This tracing is Sinus Tachycardia. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is fast (> 100 bpm). Notice that the P wave is normal, may merge with t wave at very fast rates. The PR interval is normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). QT interval shortens with increasing heart rate. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Premature Ventricular Complex Bigeminy. Look for rhythm that is irregular, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is absent. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically wide (> 0.10 sec), bizarre appearance. PVC appears every second beat. Wandering baseline artifact can be seen in this tracing. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Junctional Escape Rhythm. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is slow (40-60 bpm). Notice that the P wave is present before, during (hidden) or after qrs, if visible it is inverted. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). That's correct! This tracing is Premature Atrial Complex. Look for rhythm that is irregular, with heart rate that is usually normal but depends on underlying rhythm. Notice that the P wave is premature, positive and shape is abnormal. The PR interval is normal or longer. The QRS is typically 0.10 sec or less. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Normal Sinus Rhythm. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is normal (60-100 bpm). Notice that the P wave is normal (positive & precedes each qrs). The PR interval is normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). Wandering baseline artifact can be seen in this tracing. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Premature Ventricular Complex. Look for rhythm that is irregular, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is absent. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically wide (> 0.10 sec), bizarre appearance. Two PVCs together are termed a couplet while three PVCs in a row with a fast rhythm is ventricular tachycardia. That's correct! This tracing is Asystole. Look for rhythm that is not present, with heart rate that is absent. Notice that the P wave is absent. The PR interval is absent. The QRS is typically absent. Confirm with multiple leads. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Sinus Arrest. Look for rhythm that is irregular due to pause, with heart rate that is normal to slow. Notice that the P wave is normal. The PR interval is normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). Pause time is not an integer multiple of the P-P interval. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Third Degree Heart Block. Look for rhythm that is regular, but atrial and ventricular rhythms are independent, with heart rate that is characterized by atrial rate usually normal and faster than ventricular rate. Notice that the P wave is normal shape and size, may appear within qrs complexes. The PR interval is absent: the atria and ventricles beat independently.. The QRS is typically normal, but wide if junctional escape focus. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Third Degree Heart Block. Look for rhythm that is regular, but atrial and ventricular rhythms are independent, with heart rate that is characterized by atrial rate usually normal and faster than ventricular rate. Notice that the P wave is normal shape and size, may appear within qrs complexes. The PR interval is absent: the atria and ventricles beat independently.. The QRS is typically normal, but wide if junctional escape focus. This tracing is First Degree Heart Block. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is the underlying rate. Notice that the P wave is normal. The PR interval is prolonged (>0.20 sec). The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). A first degree AV block occurs when electrical impulses moving through the Atrioventricular (AV) node are delayed (but not blocked). First degree indicates slowed conduction without missed beats.. https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill That's correct! This tracing is Accelerated Junctional Rhythm. Look for rhythm that is regular, with heart rate that is normal (60-100 bpm). Notice that the P wave is present before, during (hidden) or after qrs, if visible it is inverted. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS is typically normal (0.06-0.10 sec). Muscle tremor noise is present in this tracing.