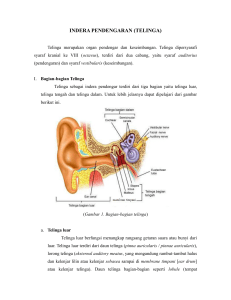
TM1-Pertemuan-7 - Terminologi Medis 1
advertisement

TM SISTEM MATA DAN TELINGA PERTEMUAN 7 DR MAYANG ANGGRAINI PRODI MIK, FAKULTAS ILMU-ILMU KESEHATAN KEMAMPUAN AKHIR YANG DIHARAPKAN • Memahami ejaan istilah struktur dan fungsi, berbagai akar kata (Root), definisi/arti dan ejaan istilah medis umum, medis penyakit/gangguan, berikut istilah diagnostik dan terapi-operasi sistem mata dan telinga. SENSORY SYSTEM: THE EYE STRUKTUR dan FUNGSI MATA • Bola mata terletak di dalam rongga orbit mata di bagian depan tengkorak kepala. • Struktur mata terbagi dalam 3 lapisan (tunics). • Struktur menjalankan fungsi untuk menerima sinar cahaya, membelokkan (refraksi) sinar cahaya terkait, dan mentransmisinya ke saraf sebagai impuls yang dibangkitkan oleh sinar cahaya ke lobus opticus otak. SENSORY SYSTEM: THE EYE (Lanjutan) Begitu cahaya sampai lobus occipital, mereka diinterpretasi sebagai gambar bayangan yang dilihat mata. Visi mata sangat bergantung pada: kesehatan mata kita, pengelihatan berkaitan dengan saraf, dan otak kita. AKAR KATA ORGAN MATA Akar Kata Definisi Contoh Istilah B. Penggabung aque/o- = watery (cair mirip air) aqueous humor blephar/o- = eyelid (kelopak mata) blepharoptosis conjuntiv/o- = conjunctiva (konjuntiva) conjunctivitis corne/o- = cornea (kornea) corneoblepharon dacry/odacrycyst/o- = tears (air mata) = tear sac (kantung a. mata) dacryoma dacryocele / dacrocystocele (Lanjutan-1) Akar Kata glauc/o- Definisi Contoh Istilah B. Penggabung = silver, gray (keperakan) glaucoma ir/o-; irid/o- = iris iridectomy kerat/o- = kornea keratoconjunctivitis lacrim/o- = air mata lacrimation ocul/o- = mata oculomycosis ophthalm/o- = mata ophthalmoplegia (Lanjutan-2) Akar Kata B. Penggabung opt/o Definisi Contoh Istilah = mata, vision optic, optical palpebr/o = kelopak mata palpebra,palpebral phac/o-; phak/o- = lensa mata phacometer phot/o- = light (cahaya) photophobia pupill/o- = pupil mata pupillometer (Lanjutan-3) Akar Kata B. Penggabung retin/o- Definisi Contoh Istilah = retina retinopathy retinitis retinoscopy scler/o- = sclera, sklera (keras) scleroplasty sclerokeratitis uve/o = uvea uveitis vitre/o- = glassy; yelly-like corpus vitrium STRUKTUR MATA Struktur mata terbagi menjadi 3 lapisan tunics: lapisan terluar = Sclera lapisan tengah = Choroid lapisan terdalam = Retina Pada masing lapisan ada struktur tambahan yang mempunyai fungsi spesifik terkait pengelihatan. (Lihat gambar: Mata) (Lanjutan-1) Lapisan terluar, terdiri dari: - Sclera: jaringan fibrosa kuat pembentuk tampilan bola mata, dan pelindung bagian terluar mata - Cornea: bagian transparan (luar) mata penutup iris mata - Conjunctiva: selaput mukosa pembatas bagian luar mata serta bagian dalam kelopak mata. (Lanjutan-2) • Lapisan tengah, terdiri dari: Choroid: lapisan jaringan di bawah sklera yang mengandung banyak pembuluh darah dan saraf. Iris: otot mengelilingi pupil mata,menimbulkan warna khusus mata. Iris mengatur lebar lobang bulatan pupil untuk mengontrol sinar cahaya yang lewat. Pupil: bulatan bagian tertengah mata Crystalline lens: kedudukan lensa dihubungkan ke choroid oleh Corpus cilliaris yang ditahan oleh Suspentory ligaments Choroid, iris, corpus cilliaris menjadi satu kesatuan yang disebut; UVEA (Lanjutan-4) Lapisan Terdalam: - Retina: jaringan saraf sensoris yang membungkus bagian dalam mata, terdiri dari susunan sel saraf rods & cones, yang mengkonversi gelombang sinar menjadi impuls saraf. - Rods: bertanggungjawab terhadap visi (ketajaman pengelihatan) pada cahaya redup dan periferal Cones: bertanggungjawab terhadap visi pada cahaya terang, sentral dan warna. - Optic disk (discus opticus): area di belakang mata tempat berhentinya ujung saraf mata yang berasal dari retina bersatu menjadi Nervus Opticus (Saraf cranialis ke 2) - Nervus opticus menstranmisi impuls ke lobus occipitalis otak besar (cerebrum). CAVITIES of the EYE Bagian interior mata ada 2 (dua) kavitas: (1) Anterior cavity: terdiri dari anterior chamber yang ada di depan lensa dan postrior chamber yang ada di bagian area di belakang lensa. (2) Posterior cavity: cavitas terisi substansi bening seperti jelly yang disebut Vitreus humor yang membentuk fisik bola mata. Vitreous humor diperlukan untuk pengelihatan, apabila bola mata cedera dan cairan ini mengalir keluar maka akan mengakibatkan: kebutaan. Agueous dan vitreous humor membantu pembiasan sinar cahaya sewaktu melintas masuk ke bola mata menuju ke retina. Cont.• When an object is near, the lens is shortened and becomes thicker; when an object is distant, the lens is lengthened and become thinner. • Ametropia is a general term that means the eye has a refractive error (an error in focusing), such as: myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism or anisometropia. • None of these is a disease in the ordinary sense of the word, they are caused simply by: variations of shape and focusing ability of the eye. Reading: The Eye HYPEROPIA Hyperopia (farsightedness): light rays focus behind the retina tends to run in the families. Mild and moderate in the young is overcome by accommodation correction can be done by glasses or contact lens with convex lenses to reinforce focusing power. (CONT.- 2) MYOPIA Myopia (nearsightedness): light rays focus in the front of the retina. uncorrected myopia, the images of distant objects are focused in front of the retina and appear blurred reduced by a concave (negative) lens Reading: The Eye (Cont.-3) • Presbyopia is the progressive loss of accomodation (ability to focus at near range) with age. • Amblyopia (poor vision in one eye without any obvious structural abnormality) (lazy eye) is often due to strabismus. • The external eye: Behind the brilliant transparency of the cornea is the fluid-filled front chamber of the eye. At the back is the iris, with the round pupil in the center. Reading: The Eye (Cont.-4) • Movement of the eye: Movement of each eyeball occurs as the result of contraction of one or more of the muscles attached around it. There are six of these muscles, each one of which pulls the eye in a specific direction. • Investigation: Because of the transparency of its structures, the eye is particularly accessible for examination. Many of the disease processes affecting it can be viewed directly by use of the ophthalmo-scope and slit lamp. Photography of the retina and fluorescein angiography are also used. Reading: The Eye (Cont.-6) • Disorders of eyelashes: Eyelashes are arranged in two rows at the front edge of each lid and curve outward. Growth in an abnormal direction may due to injury to the lid or, more commonly, infection. Occasionally. Lashes grow in an abnormal direction for no obvious reason. With age, the lashes become finer. Reading: The Eye (Cont.-7) • Severe blepharitis (eyelid infection) may cause the lid margins to be so damaged that lash roots are destroyed. Trachoma, an eye infection in which the lid is distorted by scarring, may lead to trichiasis, a condition in which the lashes turn inward. They may rub against the cornea, causing corneal abrasion. • Eyestrain: A term often used to describe aching or discomfort in the eye. Eyestrain is not accept the popular belief that the eyes can be damaged by being used. Eye drops Medication in solution for the treatment of the eye disorders or to aid in diagnosis. To use eye drops, the lower lid is held away from the eye and the drop allowed to fall behind it. Care should be taken to avoid touching the skin or eye with the dropper to reduce the risk of contamination. Common examples of drugs given in this form are: antibiotics, corticosteroids, antihistamines, drugs to control glaucoma, and drugs to dilate or constrict the pupil. STRUKTUR ASESORIS MATA Struktur asesori mata meliputi: - orbit = eye socket (bagian tulang) eyebrows (alis mata) eyelids (kelopak mata, atas dan bawah) eyelashes (bulu mata) oil glands (kelenjar minyak) = meibomian glands antara conjunctiva dan jaringan kedua kelopak mata (Lanjutan) - lacrimal glands (kelenjar air mata) (di bagian luar) fluid (cairan) lacrimal sacs (kantung) (bagian duct yang melebar) lacrimal ducts. Nasolacrimal duct Fungsi struktur asesori adalah melindungi mata dari penyakit dan cedera. ISTILAH MEDIS TERKAIT MATA Istilah medis terkait mata terbagi dalam 3 (tiga) kategori utama: (1) (2) (3) Istilah medis umum Istilah medis penyakit dan kondisi Istilah medis prosedur diagnostik, operasi, test-test laboratorium. (Lanjutan) Contoh: Roots dan Prefixes untuk Mata: Root: Arti blast/o- = imatur dipl/o- = dua/dobel fund/o- = fundus Prefix ecten-; esoex intrapresby- Arti = di luar/bagian Luar = dalam/ke dalam = luar/ke luar (dasar) = di dalam = tua Contoh Suffixes untuk Mata Suffix -ectomy -ist -itis -metry -opia -(o)tomy -pathy -plasty -ptosis Arti = operasi mengangkat = spesialis = inflamasi = mengukur = visi = insisi ke dalam = penyakit = operasi perbaikan = jatuh/turun Suffix Arti -scope = instrumen untuk melihat -tropia = membelok -tropion = pembelokan ISTILAH MEDIS UMUM MATA • • • • • • • • • • Istilah intraocular lacrimal miotic nasolacrimal ophthalmologsit ophthalmology optician optometrist optometry • visual acuity Arti = berkaitan dengan bag. dalam mata = berkaitan dengan air mata = berkaitan konstriksi pupil (obat) = berkaitan dengan hidung dan saluran air mata = spesialis mata = ilmu penyakit mata = ahli kacamata = dokter optometry = mengukur dan mentest ketajaman pengelihatan dan koreksi lensa = ketajaman pengelihatan ISTILAH PENYAKIT & GANGGUAN MATA Istilah Definisi astigmatism = eror refraksi mata yang mengakibatkan sinar cahaya tidak terfokus normal di retina, disebabkan oleh bentuk kornea yang tidak normal. Kode ICD-10 (67) (compound)(congenital)(any type) H52.2 [400] H52 Disorders of refraction & accommod. H52.0 Hypermetropia H52.1 Myopia Exc.: ... H52.2 Astigmatism (Lanjutan-1) Istilah Definisi blepharitis = inflamasi kelopak mata Kode ICD-10 (79) (angularis)(ciliaris)(eyelid)(marginal)(nonulcerative)(squamous) ulcertaive) H01.0 H01 Other inflammation of eyelid [380] H01.0 Blepharitis. Excl.: .... blepharoptosis = kelopak mata menurun Kode ICD-10 (79) H02.4 - congenital Q10.0 [380] H02.4 Ptosis of eyelid (Lanjutan-2) Istilah Definisi cataract = pengeruhan progresif lensa mata Kode ICD-10 (99) (cortical)(immature)(incipient) (see also Cataracta) H26.9 (100) Cataracta (see also Cataract) H26.9 [390] H26 Other cataract Excl.: ... H26.0 s/d H26.4, H26.8 H26.9 Cataract, unspecified (Lanjutan-3) Istilah Definisi chalazion = benjolan/kista di kelopak mata yang timbul akibat kelenjar meibomian tersumbat Kode ICD-10 (102) H00.1 [380] H00 Hordeolum and chalazion H00.0 Hordeolum & other deep inflam. ... H00.1 Chalazion conjunctivitis = inflamasi konjungtiva Kode ICD-10 (152) (in)(due to) H10.9 [383] H10.9 Conjunctivitis, unspecified. (Lanjutan-4) Istilah Definisi dacryocystitis = inflamasi pada kantung air mata Kode ICD-10 (172) (acute)(phlegmonous) H04.3 [382] H04.3 Acute and unspecified inflammation of lacrimal passages Excl.: ... detached retina/ = retina lepas dari lapisan choroid ablatio retina mata Kode ICD-10 (199) Detachment retina (without retinal break) H33.2 - with retinal break H33.0 [392] H33.0 atau H33.2 (ada/tidak retinal break) (Lanjutan-5) Istilah color blind Definisi = tidak mampu mengenal warna tertentu (tidak bisa “melihat”) Kode ICD-10 (79) Blind - see also Blindness Blindness color H53.5 [401- 402] H53.5 Colours vision deficiencies. Excl.: diabetic retinopathy = gangguan retina berikut pembuluh Darahnya pada DM yang tak terkontrol dengan baik Kode ICD-10 (555) diabetic (see also E10-E14 with 4th character .3) E14.3 H36.0* [252-254] Unspecified DM with ophthalmic complication (retinopathy). (Lanjutan-6) Istilah Definisi diplopia = visi dobel/pengelihatan dobel Kode ICD-10 (204) H53.2 [401] H53.2 Diplopia Double vision ectropion = margin bulu mata terbalik ke luar (> pada kelopak bawah) Kode ICD-10 (245) H02.1 [380] H02 Other disorders of eyelid Excl.: congenital malformation of eyelid (Q...) H02.1 Ectropion of eyelid (Lanjutan-7) Istilah Definisi entropion >< ectropion Kode ICD-10 (259) (cicatrical)(eyelid)(paralytic) (senile)(spastic) H02.0 [380] H02.0 Entropion and trichiasis of eyelid esotropia = starbismus konvengens (cross-eyed) Kode ICD-10 (264) (alternating)(monocular)H50.0 [399] H50.0 Convergent concomitant strabismus exophthalmia (exophthalmos) = mata menonjol ke Kode ICD-10 (267) H05.2 luar. [382] H05.2 Exophthalmic conditions (Lanjutan 8) Istilah exotropia Definisi = bola mata memutar ke luar (divergent strabismus) (walleyed) Kode ICD-10 (267) (alternating)(monocular) H50.1 [399] H50 Other strabismus H50.1 Divergent concomitant strabismus Exotropia (alternating)(monocular), except intermittent strabismus = juling Kode ICD-10 (593) (alternating)(congenital)(nonparalytic) H50.9 [400] H50.9 Strabismus, unspecified (Lanjutan-9) Istilah Definisi glaucoma = tekanan intraocular meninggi Kode ICD-10 (297-298) H40.9 [395] H40.9 Glaucoma, unspecified. hordeolum = infeksi bakterial pada kelenjar minyak atau folikel bulu mata (sty) (bintiten) Kode ICD-10 (324) (eyelid)(external)(internal) (recurrent) H00.0 [380] H00.0 Hordeolum and other deep inflammation of eyelid (abscess, furuncle, Stye) of eyelid (Lanjutan 10) Istilah Definisi iritis = inflamasi dari iris mata Kode ICD-10 (381) (see also Iridocyclitis) H20.9 [387] H20.9 Iridocylitis, unspecified keratitis = inflamasi dari kornea mata Kode ICD-10 (386) (nonulceration) H16.9 [385] H16.9 Keratitis, unspecified hyperopia = gangguan pengelihatan jarak dekat (rabun dekat) Kode ICD-10 (330) H52.0 [400] H52.0 Hypermetropia (Lanjutan 11) Istilah Definisi myopia gangguan pengelihatan jarak jauh (rabun jauh) Kode ICD-10 (433) (axial)(congenital)(progressive) [400] H52.1 Excl.: degenerative myopia (H44.2) nyctalopia = = gangguan pengelihatan pada malam hari Kode ICD-10 (481) (night blindness) H53.6 - vitamin A deficiency E50.5 H58.1* [264] E50.5 Vit. A deficiency with night blindness [404] H58.1* Visual disturbances in diseases classified elsewhere. (Lanjutan 12) Istilah Definisi photophobia = peka abnormal terhadap cahaya (silau) Kode ICD-10 (513) Photophobia H53.1 [401] H53.1 Subjective visual disturbances Excl: visual hallucinations (R44.1) photoretinitis= kerusakan atau peradangan retina akibat terlampau banyak terpajan sinar cahaya Kode ICD-10 (513) H31.0 [391] H31.0 Chorioretinal scare; solar retinopathy (Lanjutan-13) Istilah Definisi presbyopia = gangguan membaca pada jarak yang umum (kira-kira jarak satu kaki dari mata), karena lanjut usia (akibat elastisitet lensa menurun) Kode ICD-10 (533) H52.4 [400] H52.4 Presbyopia pterygium = pertumbuhan iregular disertai penebalan konjungtiva di daerah nasal kornea mata Kode ICD-10 (543) (eye) H11.0 [383] H11.0 Pterigium. Excl.: pseudopterygium (Lanjutan-14) Istilah Definisi retinitis pigmentosa = penyakit degenerasi retina tanpa inflamasi mengganggu pengelihatan malam hari disertai penyempitan medan pengelihatan. Kode ICD-10 (555) pigmentosa H35.5 [394] H35.5 Hereditary retinal dystrophy retinoblastoma = tumor ganas retina Kode ICD-10 (555) (M9510/3) C69.2 [1046] M9510/3 Retinoblastoma NOS (C69.2) [190] C69.2 Retina C69 Malignant neoplasm of eye and adnexa Excl.: .... (Lanjutan-15) Istilah Definisi retinopathy = gangguan/penyakit retina Kode ICD-10 (555) (background)(Coats)(exudative) (hypertensive) H35.0 [393] H35.0 Background retinopathy and retinal vascular changes. nystagmus = gerak involunter mata yang bisa dirasakan atau tidak dirasa oleh yang bersangkutan Kode ICD-10 (481) (congenital)(deprivation) (dissociated)(latent) H55 [404] H55.X Nystagmus and other irregular eye movements (Lanjutan-16) Istilah Definisi sclerokeratitis = inflamasi sklera dan kornea Kode ICD-10 (567) H16.8 [385] H16.8 Other keratitis strabismus = mata tidak mampu untuk memandang lurus ke satu arah akibat kelemahan otot mata (juling/kero) Kode ICD-10 (593) (alternating)(congenital)(nonparalytic) H50.9 [400] H50.9 Strabismus, unspecified (Lanjutan-17) Istilah Definisi trachoma = infeksi kronik menular pada konjungtiva dengan tanda dan gejala hipertrofi dari konjungtiva Kode ICD-10 (624) trachomatous A71.9 [127-128] A71.9 Trachoma, unspecified. uveitis = inflamasi pada iris, corpus cilliaris dan choroid mata. Kode ICD-10 (646) (anterior)(see also Iridocyclitis) [387] H20.9 Iridocyclitis, unspecified ISTILAH TIDANKAN DIAGNOSTIK & TERAPI MATA Istilah blepharoplasty corneal transplant cryoextraction of the lens enucleation of the eye extracapsuar cataract extraction (ECCE) funduscopy iridectomy Definisi = operasi plastik kelopak mata = transplantasi kornea mata = mengangkat lensa mata dengan alat (probe) pendingin = mengangkat bola mata dari orbit = mengangkat lensa berserta segmen anterior kapsul lensa = memeriksa bagian fundus mata (belakang dari bagian dalam mata) dengan ophthalmoscope = eksisi iris mata (Lanjutan-1) Istilah Definisi intraocular lens implant = implantasi lensa mata, umumnya bersamaan dengan ekstraksi katarak keratoplasty = operasi plastik kornea ophthalmoscope = instrument untuk melihat ke bagian dalam mata ophthalmoscopy = proses pemeriksaan mata bagian interior (dalam) phacoemulsification = penghancuran lensa mata/ katarak menjadi partikel halus yang bisa disedot keluar (sucction/aspiration) (Lanjutan-2) Istilah Definisi photo-refractive = pengangkatan sel-2 lapisan kornea untuk mengkoreksi keratectomy (PRK) keadaan myopia radical keratomy (RK) = spokelike incisions ke dalam kornea untuk mengkoreksi rabun jauh retinal photocoagulation = operasi plastik retina untuk mengkoreksi retina yang lepas (detachment) dan mencegah perdarahan pembuluh darah retina. (Lanjutan-3) Istilah scleral bucking Definisi = perbaikan retina lepas dengan menreseksi atau melipat sclera ke dalam trabeculectomy = eksisi bagian kornea dan jaringan sklera untuk mengurangi tekanan intraocular virectomy = pengangkatan semua bagian vitreuos humor Code ICD-9-CM Vol 3 1. blepharoplasty - see also Reconstruction, eyelid 08.70 2. Funduscopy 3. iridectomy - (basal)(buttonhole)(optical)(perpheral) (total) 12.14 - with ... - capsulectomy 13.65 dst. 4. Keratoplasty - (tectonic)(with autograft)(with homograft) 11.60 dst. (Lanjutan-1) 5. ophthalmoscopy - 16.21 6. vitrectomy - (mechanical)(posterior approach) 14.74 - with scleral buckling 14.49’ - anterior approach 14.73 7. photocoagulation - ciliary body 12.73 - eye, eyeball 16.99 - iris 12.41 - orbital lesion 16.92 dst. 8. enucleation - see also Excission, lesion, by site - eyeball 16.49 - - with implant (into Tenon’s capsule) 16.42 with attachment of muscles 16.41 - - (Lanjutan-3) 9. phacoemulsification (ultrasonic)(with aspiration) 13.41 10. cryoextraction , lens - see also Extraction, cataract, intracapsular 13.19 Extraction lens (eye) - see also Extraction, cataract 13.19 13.19 Other intracapsular extraction of lens Cataract extraction NOS Cryoextraction of lens Erysiphake extraction of cataract Extraction of lens NOS ABBREVIATIONS • Abbreviation EOM ICCE IOL IOP OD OS OU PERRLA PRK REM RK VA VF Istilah lengkap = extraocular movement = intracapsular cataract extraction = intraocular lens = intraocular pressure = oculus dextra (dexter) = oculus sinistra (sinister) = oculus uterque (each eye) = pupil equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation = photo-reactive keratectomy = rapid eye movement = radical keratotomy = visual acuity. = visual field SISTEM SESORIS: TELINGA • Struktur telinga terdiri dari: - Bagian terluar di kanan kiri kepala disebut External ear (telinga luar) • Struktur internal terletak di dalam tengkorak kepala terbagi menjadi: Middle ear (telinga tengah) Inner ear (telinga dalam) • Secara menyeluruh struktur telinga berfungsi untuk menjalankan tugas: (1) menerima sensoris pendengaran (2) menjadi organ sensoris kesetimbangan tubuh HEARING PATHWAY Suara masuk telinga ke bagian tengah ke bagian dalam, di sini diubah jadi impuls listrik ditransmisi ke cortex cerebri untuk di-interpretasikan sebagai pendengaran. AKAR KATA: TELINGA • Akar Kata B. Penggabung acoust/oaudio/ocochle/olabyrinth/omyring/oot/ostaped/o- tympan/o- Definisi = = = = = = = hearing (pendengaran) pendengaran; suara cochlea (koklea) inner sac; labyrinth (telinga tengah) eardrum (genderang telinga) ear (telinga) stapes; middle ear bone (tulang telinga tengah) = eardrum STRUKTUR TELINGA • Telinga eksterna (luar) (external ear) meliputi: (1) auricle (pinna) = daun telinga yang terdiri dari tulang rawan, berfungsi sebagai pengarah jalan masuknya gelombang suara ke dalam telinga. (2) External cannal (auditory cannal) = saluran telinga yang terlapisi rambut cilia dan ceruminous glands (kelenjar kotoran telinga). Cilia mengatur arah gelombang suara melalui canal. Kelenjar serumen menghasilkan cerumen (earwax) berfungsi sebagai pelindung dan pelumat telinga (Lanjutan-1) (3) Tympanic membrane (eardrum) (genderang telinga) memisahkan telinga luar dari telinga tengah berfungsi mentransmisi gelombang suara ke dalam telinga tengah. Telinga tengah (middle ear) meliputi 3 (tiga) tulang kecil = Ossicles (4) malleus = bagian yang terdekat ke genderang = hammer (bentuk pukul besi). (5) incus = anvil, mirip bentuk alas pandai besi (Lanjutan-2) (6) stapes = stirrup karena mirip bentuk alas injak kaki pelana kuda, dan (7) Telinga tengah = eustachian tube yang menghubungkan telinga tengah ke pharynx. Menguap dan menelan akan membuka saluran ini untuk mengatur tekanan antara telinga tengah dan udara luar. Gelombang suara memvibrasi genderang menggerakan tulangtulang malleus mentransmisi ke incus stapes memvibrasi ke (8) oval window = penyekat batas telinga tengah dan dalam. (Lanjutan-3) • Telinga bagian dalam labyrinth meliputi: (9) vestibule (10) semicircular cannals (11) cochlea yang berbentuk spiral mirip rumah siput terisi: cairan dan organ corti. (Lanjutan) Organ corti berfungsi sebagai penerima vibrasi suara dan mengkonversi ke dalam impuls saraf yang oleh saraf acoustic diteruskan ke otak dan dikenal sebagai suara khusus. Canalis semisirkularis berlanjut ke vestibul dan berisi cairan yang diperlukan untuk kesetimbangan (balance) tubuh dan keseimbangan (equilibrium). TERMINOLOGI MEDIS terkait TELINGA Istilah medis telinga dikelompokkan menjadi 3 (tiga): (1) (2) (3) Istilah medis umum Istilah medis penyakit atau gangguan Istilah medis prosedur: - diagnostik, - operasi, - tes-tes laboratorium. (Lanjutan) Akar kata/ b. penggabung Arti Suffix Laryng/o- = larynx -cusis; cusia pendengaran Myc/o- = jamur -oma Rhin/o- = hidung -rrhae -(o)tomy -plasty -metry -gram Arti tua/ manula Prefix Old Arti tumor aliran ke luar insisi ke dalam operasi plastik mengukur gambar ISTILAH MEDIS UMUM terkait TELINGA Istilah Acoustic Audiologist Audiology Auditory Cochlear Otologist Otorhinolaryngologist Otorhinolaryngology Otology Otoscope Arti = terkait pendengaran = seorang spesialis pengevaluasi ketajaman pendengaran dan tuli = ilmu tentang pendengaran = terkait pendengaran = terkait cohlea telinga = dokter spesialis ilmu pengobatan penyakit/gangguan telinga = dokter spesialis THT = ilmu ENT (THT) = ilmu telinga = alat untuk memeriksa telinga. ISTILAH MEDIS PENYAKIT/ GANGGUAN TELINGA (Kode ICD-10) ISTILAH DEFINISI 1. acoustic neuroma = tumor benign saraf akoustik Kode ICD-10 (476) (nerve) (M9560/0) D33.3 [1046] M9560/0 Neurilemmoma NOS [218] D33.3 Benign neoplasm, Cranial nerves, olfactory bulb. (???) 2. cholesteatoma = masa kistik/tumor yang tumbuh lambat, terjadi dari kumpulan debris epitel dan cholesterol, sering timbul di telinga tengah Kode ICD-10 (105) H71 [412] H71 Cholestetoma of middle ear Incl.: ... Excl.: ... (Lanjutan-1) ISTILAH DEFINISI 3. impacted cerumen = akumulasi eksesif cerumen Kode ICD-10 (102) Cerumen (accumulation) (impacted) H61.2 [409] H61.2 Impacted cerumen (wax in ear) 4. conductive deafness = tuli akibat gangguan transmisi gelombang suara melalui telinga luar/tengah Kode ICD-10 (173) H90.2 [415] H90.2 Conductive hearing loss, unspecified Conductive deafness NOS (Lanjutan-2) ISTILAH DEFINISI 5. labyrinthitis = inflamasi atau infeksi telinga dalam Kode ICD-10 (391) (circumscribed)(destructive) (diffuse)(inner ear)(latent)(purulent) (suppurative) H83.0 [414] H83.0 Labyrinthitis 6. Meniere’s diseases = penyakit kronik telinga dalam dengan gejala akumulasi eksesif cairan di dalamnya. Kode ICD-10 (420) , syndrome or vertigo H81.0 [413] H81.0 Meniere disease (Baca Excl.: pada H81) (Lanjutan-3) ISTILAH DEFINISI 7. myringitis = inflamasi atau infeksi genderang telinga Kode ICD-10 (433) H73.8 [412] H73.8 Other specified disorders of the tympanic membrane 8. otalgia/earache = sakit telinga Kode ICD-10 (492) H92.0 (244) earache H92.0 [416] H92.0 Otalgia (Lanjutan-4) ISTILAH DEFINISI 9. otitis externa = radang atau infeksi saluran telinga luar (swimmer’s ear) Kode ICD-10 (493) H60.9 acute H60.5 chronic H60.8 [408] H60.9 Otitis externa, unspecified. 10. otitis media = radang atau infeksi telinga tengah. Kode ICD-10 (493) H66.9 (acute, chronic, subacute) [411] H66.9 Otitis media, unspecified (NOS, acute NOS, chronic NOS) (Lanjutan-5) ISTILAH DEFINISI 11. otomycosis = infeksi telinga luar akibat jamur (di external auditory meatus) Kode ICD-10 (493) (diffuse)(in) B36.9 H62.2* [409] H62.2* Otitis externa in mycoses Otomycosis NOS (B36.9 ) 12. otorrhea = pengeluaran cairan dari telinga Kode ICD-10 (493) H92.1 [416] H92.1 Otorrhoea Excl.: traumatic otorrhagia – code by type of injury. (Lanjutan-6) ISTILAH DEFINISI 13. otosclerosis = kekakuan telinga (bagian stapes) Kode ICD-10 (493-494) H80.9 [413] H80.9 Otosclerosis, unspecified. 14. perforation of the tympanic membrane = genderang telinga ruptur atau berlobang Kode ICD-10 (505 – 507) (persistent post traumatic) (post inflammatory) H72.9 - traumatic S09.2 [412] H72.9 Perforation of t. Membrane, unspec. (Lanjutan-7) ISTILAH DEFINISI 15. presbycusis = gangguan pendengaran pada manula Kode ICD-10 (533) presbyacusia H91.1 [415] H91.1 Presbycusis (presbyacusia) 16. sensoneural deafness = tuli sensoneural akibat kerusakan sel saraf auditori atau jaringan Kode ICD-10 (173) – sensorineural H90.5 [415] H90.5 Sensorineural hearing loss, unspecified Congenital deafness NOS dst. (Lanjutan-8) ISTILAH DEFINISI 17. serous otitis media = infeksi telinga tengah disertai akumulasi cairan serosa (jernih/bening) Kode ICD-10 (493) Otitis media acute serous H65.0 Otitis media chronic serous H65.2 [409 – 410] H65.0 Acute serous otitis media H65.2 Chronic serous otitis media 18. suppurative otitis media = infeksi telinga tengah disertai pengeluaran nanah OM acute suppurative H66.0 OM chronic suppurative H66.3 (Lanjutan-9) ISTILAH DEFINISI 19. tinnitus = sensasi mendengung di telinga Kode ICD-10 (622) (audible)(aurium)(subjective) [416] H93.1 Tinnitus 20. tympanitis = radang pada membrane tympani Kode ICD-10 (638-639) H73.8 [412] - chronic H73.1; acute H73.0 21. vertigo = pusing, terasa terputar-putar. Kode ICD-10 (650) R42 ( baca rinciannya!) ISTILAH MEDIS TINDAKAN DIAGNOSTIK dan TERAPI Istilah audiogram audiometry myringoplasty myringotomy Definisi = gambar grafik ketajaman pendengaran = instrumen pengukur ketajaman pendengaran = operasi plastik perbaikan genderang telinga = insisi genderang telinga myringotomy and tubes = insisi genderang telinga disertai insersi tube / untuk jalan mengalir keluar cairan otoplasty = operasi plastik perbaikan satu atau kedua telinga ISTILAH MEDIS TINDAKAN DIAGNOSTIK dan TERAPI (Lanjutan) Istilah otoscopy Definisi = menggunakan otoscope untuk melihat keadaan genderang telinga Rinne test = test pembeda konduksi gelombang suara melalui tulang dan udara dengan alat garpu tara Stapedectomy = insisi stapes telinga Tympanoplasty = operasi plastik perbaikan genderang telinga Tympanotomy = insisi genderang telinga Weber test = pemeriksaan ketajaman pendengaran penentu adanya gangguan akibat defisit Konduktif atau sensoneural ABBREVIATIONS Abbreviations Arti AC = air condition AD = auris dextra (telinga kanan) AS = auris sinistra (telinga kiri) AU = auris unitas (masing telinga) BC = bone conduction (konduksi tulang) BOM = bilateral otitis media EENT = eyes, ears, nose, throat ENT = ear, nose, throat TM = tympanic membrane READING 1: OTITIS MEDIA • Inflammation of the middle ear (the cavity between the eardrum and the inner ear) Causes: The inflammation occurs as the result of an upper respiratory tract infection, extending up the eustachian tube, the passage that connects the back of the nose to the middle ear. • The tube may become blocked by the inflammation or sometimes by enlarged adenoids, which are often associated with infections of the nose and throat. As a result, fluid produced by the inflammation along with pus in bacterial infections is not drained off through the tube but accumulates in the middle ear. Reading: (Cont.-2) The chronic phase of otitis media (otitis media with effusion) follows an upper respiratory infection that has produced acute otitis media. Incidence: Children are susceptible by otitis media, probably because of the shortness of their eustachian tubes. About one in six children suffers from the acute form in the first year of life about one in 10 in each of the next six years. Some children have recurrent attacks. Chronic otitis media is much less common because, in most cases, attacks of acute middle-ear infection clear with treatment. Reading (Cont.-2) Symptoms and Signs Acute otitis media is marked by sudden, severe otalgia, a feeling of fullness in the ear, deafness, tinnitus, and fever. Sometimes the eardrum bursts, relieving the pain and resulting in an otorrhea of pus. In this case, healing usually occurs in several days. In chronic otitis media, pus constantly exudes from a perforation in the eardrum and there is some degree of deafness. Complication of the condition include otitis externa, damage to the bones in the middle ear, causing more deafness (sometime total) in the affected ear; or a cholesteatoma. In rare cases, infection spreads inward from an infected ear causing mastoiditis or a brain abscess Reading (Cont.-4) Diagnosis The diagnosis is usually made from examining the ears with an otoscope. A swab may be taken of any discharge so that the organism responsible for the infection can be cultured and identified. Treatment: AOM is treated by giving antibiotic drugs and analgesics. Usually the condition clears up completely with treatment, but in some cases there is continual production of sticky fluid in the middle ear, a condition known as persistent middle-ear effusion Reading (Cont.-6) COM is treated by sucking out pus and infected debris from the ear as necessary. Antibiotic ear drops may be given if this does not adequately control the condition. Medical Terms: Otoplasty = ... Otorrhea = .... Otosceloris (> inherited) =progressive conductive deafness. 1/200 started in early adulthood, > women than men, often develops during pregnancy) Ototoxicity = keracunan telinga (kerusakan bisa pada cochlea dan canalis semicircularis dalam telinga dalam) gangguan pendengaran dan kesetimbangan Otoscope = ... READING 2: DEAFNESS Complete or partial inability to hear. Total deafness is rare and is usually congenital. Partial deafness, ranging from mild to severe, is most commonly the result of : an ear disease, injury, or degeneration of the hearing mechanism with age. (Cont.-) All deafness is either conductive or sensorineural. Conductive deafness is faulty transportation of sound from the outer to the inner ear, usually due to damage to the eardrum or the three connected bones in the middle ear – the malleus, incus and stapes. In sensorineural deafness, sounds that reach the inner ear fail to be transmitted to the brain because of damage to the structures within the inner ear or to the acoustic nerve, which connects the inner ear to the brain. (Cont.-) Causes: Conductive deafness: In an adult, the most common cause of conductive deafness is earwax blocking the outer ear canal. Less commonly, otosclerosis (the stapes loses its normal mobility) may be responsible. In a child, OM is by far the most common cause of this types of deafness. READING 2: DEAFNESS (Cont.-2) Rarely, conductive deafness can be caused by barotrauma, or by a perforated eardrum as the result: of injury, a middle-ear infection, or surgery on the ear. • Sensorineural deafness: Defects of the inner ear are sometime congenital due: to an inherited fault in a chromosome, to birth injury, or to damage to the developing fetus – as the result of the mother having had rubella during pregnancy. Damage to the inner ear may also occur soon after birth as the result of severe jaundice. READING 2: DEAFNESS (Cont.-3) Sensorineural deafness that develops in later life can be caused by: prolonged exposure to loud noise, Meniere’ s disease (increased fluid pressure in the labyrinth), certain drugs (such as streptomycin) or by some viral infections. All damage the cochlea and/or labyrinth. These structures also degenerate naturally with old age (presbycusis) Damage to the acoustic nerve may be the result of an acoustic neuroma. As the acoustic neuroma enlarge, it causes increasing deafness.