Uploaded by
common.user93315
Sensor Types: Proximity and Photoelectric Sensors Explained
advertisement

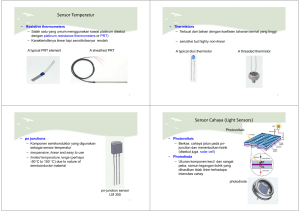
SENSOR Prepare by M Arief Rochman, S.T., M.T 3 MACAM KOMPONEN KONTROL Input Logic Output SENSOR A sensor is a device that converts a physical phenomenon into an electrical signal. -Sensor Technology Handbook- SENSOR "Sensor" is classified to the detection switch in a broad sense. A sensor is a device that controls the flow of electrical current using a solid state device such as a transistor instead of a mechanical set of contacts. Using a transistor means the sensor has a very high speed response to input changes and very long life when compared to a mechanically operated set of switching contacts. OUR DISCUSSION 1. Proximity Sensor 2. Photoelectric Sensor PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR VS PROXIMITY SENSOR There are many sensors to control the flow of electric current and they are classified by how they detect input changes. The most typical types of sensors found in factory automation are "Photoelectric" and "Proximity" sensors. "Proximity Sensors" detect an object by the change using magnetic or electric fields. "Photoelectric Sensors" detect an object when the amount of light changes. PROXIMITY SENSOR PROXIMITY SENSOR A Proximity sensor (also called "Proximity switch" or simply "PROX") responds to the presence of an object close to the sensor. In most cases this is just a few mm. Often the proximity sensor detects an end-position of a machine part and the sensor output signal triggers another function of the machine. WHY PROXIMITY SENSOR? Today proximity sensors are found in many types of industries and applications. Some examples: Automotive industry Machine tool industry Food processing industry Utility vehicles (e.g. trucks, agricultural machines) Car washing machines TYPES OF PROXIMITY SENSORS There are 2 main types of industrial proximity sensors: Inductive proximity sensors detect objects by generating an electro-magnetic field. Naturally only metal objects can be detected. Capacitive proximity sensors detect objects by generating an electrostatic capacitive field. Therefore all kinds of objects can be detected. INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR An inductive proximity sensor consists of a coil wound around a ferrite core at the sensing head. A high frequency is applied to this, generating an oscillating electro-magnetic field around it. This is monitored by an internal circuit. When a metallic object moves towards this field, electric currents (eddy currents) are created in the object. INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR These currents cause a transformer like effect, as a result the energy in the detecting coil lessens and the oscillations are reduced; the magnetic field strength is decreased. The monitoring circuitry detects the dropping level of the oscillations and then switches the output. The object has now been detected. INDUCTIVE SENSOR OUTPUT Today most inductive sensor feature transistor output with NPN or PNP logic (see picture below) . These types are also called DC-3 wire models. In some installations proximity sensors with 2 connections (plus and minus) are used. They are called DC-2 wire models (see diagram below). INDUCTIVE SENSOR NORMALLY OPEN Kondisi Awal Tidak ada benda logam Lampu mati INDUCTIVE SENSOR NORMALLY OPEN Kondisi Awal Ada benda logam Lampu menyala Perhatikan bedanya INDUCTIVE SENSOR NORMALLY CLOSE Kondisi Awal Tidak ada benda logam Lampu menyala INDUCTIVE SENSOR NORMALLY CLOSE Kondisi Awal Ada benda logam Lampu mati CAPASITIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR Capacitive proximity sensor permits non-contact detection of metallic and non-metallic objects such as glass, wood, water, oil and plastic. CAPASITIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR Capacitive proximity sensors detect objects by generating an electrostatic capacitive field. Therefore all kinds of objects can be detected. TYPE OF CAPASITIVE SENSOR Normally Open, Normally Close 3 wire / 2 wire Catatan : sama dengan inductive sensor NPN VS PNP PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR Photo electric Sensor – Counter – Indicator Lamp PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR Photoelectric sensor is an equipment used to discover the distance, absence, or presence of an object by using a light transmitter, often infrared, and a photoelectric receiver. PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR COMPONENT Light-On/Dark-On switch (1) Sensitivity adjuster (2) Receiver (3) Emitter (4) Output and Power Supply Connection (5) Indicators (6) OPERATING MODES Through-beam Retro-reflective Diffuse-reflective Background-Suppression (a type of diffuse reflective sensor) PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR : 1. THROUGHBEAM SENSORS Throughbeam sensors have separate emitter and receiver device. The emitter part of the sensor pair emits a beam of light, and the receiver part of the sensor receives the light. If an object moves in between the emitter and receiver, breaking the beam, the receiver outputs a signal. PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR : 2. RETRO-REFLECTIVE SENSOR The sensor's emitter sends out the light to a special prism reflector, which reflects the light back to the sensor's receiver. If an object moves into the path of the light, the sensor generates an output. PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR : 3. DIFFUSE REFLECTIVE SENSORS Diffuse-reflective sensing sends light from the emitter towards the sensed object. The sensed object reflects part of the emitted light (diffuse reflection) back to sensor's receive component to determine the absence or presence of the object. PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR : 4. BACKGROUND-SUPPRESSION SENSOR A background suppression sensor is a special version of a diffuse sensor. Whereas a pure diffuse sensor is detecting the amount of light received, the BGS sensor detects the angle of received light. This technology is called triangulation. Thus the sensing behaviour is not influenced by the color of the object or any backgrounds. To realize a triangulation the sensor is using a double-diode as receiver or a PSD element/diode array. WIRING PHOTOELECTRIC SENSOR WIRING DIAGRAM (PNP) JIS DIN WIRING DIAGRAM (NPN) JIS DIN ALHAMDULILLAH Sumber: 1. Sensor Technology Handbook. Jon Wilson. 2005. 2. OmronLeraning. 3. Modul pelatihan SMC.