Batuan Beku - Pendidikan Geografi UMS
advertisement

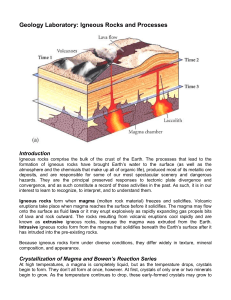
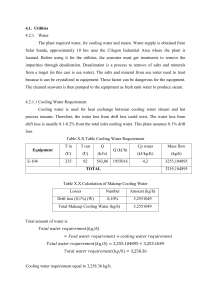
PETROLOGY 1. Description of rocks 2. Classification of rocks 3. Theories on how these rocks formed Crystallize from molten material • Magma - below the Earth's surface • Lava - erupts onto the Earth's surface through a volcano or crack (fissure) Lava cools more quickly because it is on the surface. Cooling Rates • Cooling rates influence the texture if the igneous rock: • Quick cooling = fine grains • Slow cooling = coarse grains EKTRUSIF/VULCONIK (Batuan Beku Luar) 1. Terbentuk di permukaan bumi. 2. Pembentukan mineral berjalan cepat 3. Kristalisasi tidak terjadi/kurang sempurna 4. Ukuran mineral tidak dapat dilihat dengan mata. 5. Tekstur halus INTRUSIF/PLUTONIK (Batuan Beku Dalam) 1. 2. 3. 4. Terbentuk jauh di dalam bumi. Pembentukan mineral berjalan lambat Kristalisasi sempurna Ukuran mineral dapat dilihat dengan mata. 5. Tekstur kasar Igneous textures Glassy = instantaneous cooling Obsidian (volcanic glass) • Aphanitic - fine grain size (< 1 mm); result of quick cooling Basalt Rhyolite Andesite Phaneritic coarse grain size; visible grains (1-10 mm); result of slow cooling • Granite • Diorite • Gabbro Vesicular - contains tiny holes called vesicles which formed due to gas bubbles in the lava or magma. Very porous. May resemble a sponge. Commonly low density; may float on water. Composition of Igneous Rocks 1. 2. 3. 4. Felsic (granitic or Sialic ) Intermediate (or andesitic) Mafic (or basaltic) Ultramafic Felsic (granitic or Sialic ) • • • • • Dominated by silicon and aluminum (SiAl) Usually light in color Characteristic of continental crust Rock types include: Granite, Riolite Accecories mineral :potassium feldspar (generally pink or white) , Na-plagioclase feldspar (generally white) , quartz (generally gray or colorless) , biotite Intermediate (or andesitic) Intermediate in composition between sialic and mafic Rock types include: Andesite (aphanitic) Diorite (phaneritic) Accecories mineral : plagioclase feldspar, amphibole, pyroxene, biotite, quartz Mafic (or basaltic) • Contains abundant ferromagnesian minerals (magnesium and iron silicates) • Usually dark in color (dark gray to black) • Characteristic of Earth's oceanic crust, Hawaiian volcanoes • Forms a runny (low viscosity) lava • Rock types include: Basalt, Gabbro Ultramafic • Almost entirely magnesium and iron silicates (ferromagnesian minerals) • Rock types include: Peridotite (phaneritic) – dominated by olivine - the birthstone is Peridot, which gives its name to Peridotite • Minerals commonly present include: Olivine is dominant. (Olivine is olive green). may have minor amounts of pyroxene and Caplagioclase Order of crystallization by Dr. N.L. Bowen MAFIC GABBRO This is a mafic igneous intrusive rock. DIORITE This speckled coarse-grained specimen is an intermediate composition igneous intrusive rock. GRANITE – This is a felsic intrusive rock. BASALT This typically dark, mafic to ultramafic volcanic rock is apparently featureless. The presence of olivine suggests it is ultramafic. RHYOLITE The lighter colour is indicative of the felsic composition of this extrusive rock. Kelompok Batuan Beku 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Rhyolit – Granit Trachit- Syenit Dasit-Kwarsa Dasit Andesit-Diorit Gabro-Basalt