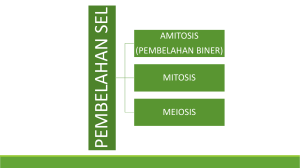
1. tujuan reproduksi sel - Jurusan Biologi FMIPA
advertisement
9/28/2016 PEMBELAHAN (REPRODUKSI) SEL UNSYIAH Universitas Syiah Kuala Pengantar Biologi MPA-107, 3 (2-1) Kuliah 3 SEL: REPRODUKSI SEL Tim Pengantar Biologi Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Unsyiah Konsep umum • Sel bereproduksi dengan cara membelah menjadi dua (2) sel anak; • Sebelum sel membelah, terjadi penggandaan bahan genetik (replikasi DNA); • Pembelahan sel menghasilkan dua (2) sel anak yg identik (tepat sama) secara genetik; • Dua (2) sel anak akan mengalami; pertumbuhan hingga dapat bereproduksi kembali menjadi dua sel anak yang baru. • Tujuan Reproduksi sel Meneruskan generasi ke Generasi ‹#› 1. TUJUAN REPRODUKSI SEL MH Multiseluler, Reproduksi sel berfungsi untuk: • • • • Makhluk hidup satu sel (UNISELULER) seperti Amoeba bereproduksi untuk memperbanyak diri dengan cara pembelahan sel Perkembangan (sejak fertilisasi); Pertumbuhan (ber+ ukuran); Perbaikan (repair) sel yang rusak. Meneruskan generasi. ‹#› Molekul DNA sebagai Informasi Genetik di dalam sel: Dikemas dalam bentuk Kromosom ‹#› • Pada persiapan pembelahan sel, DNA be-replikasi dan kromosom ber-kondensasi • Pada duplikasi kromosom • Memiliki 2 Kromatid, yg terbentuk pada waktu sel membelah • Kromosom sel eukariot • Bentuk kromatin, bentuk kompleks DNA dan protein yg mengalami kondensasi pada waktu sel membelah. • Pada hewan • Sel Somatik memiliki dua (2) set kromosom (DIPLOID) • Sel Gamet memiliki satu (1) set kromosom (HAPLOID) A eukaryotic cell has multiple chromosomes, one of which is represented here. Before duplication, each chromosome has a single DNA molecule. Once duplicated, a chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. Each chromatid contains a copy of the DNA molecule. Mechanical processes separate the sister chromatids into two chromosomes and distribute them to two daughter cells. 0.5 µm Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis) Centromere Separation of sister chromatids Centromeres ‹#› Sister chromatids Sister chromatids ‹#› 1 9/28/2016 • Pembelahan sel pada eukariot: Mitosis, Pembelahan inti sel (nucleus) Meiosis, Pada sel gamet dihasilkan jumlah kromosom mengalami reduksi Siklus sel : 1. Sel tumbuh: kromosom bereplikasi 2. Kromosom bersegregasi 3. Sel membelah Siklus sel : S-phase: (interfase): kromosom bereplikasi Mitosis: Kromosom bersegregasi Sitokinesis: Sel membelah ‹#› Diagram Siklus sel ‹#› Interfase terdiri dari subfase • G1 phase : Fase pertumbuhan 1: metabolisme • S phase: Fase Replikasi DNA • G2 phase: Fase tumbuh dan persiapan membelah ‹#› Diagram siklus sel ‹#› Contoh siklus sel pada sel ragi • Fase Mitotik terdiri dari: Mitosis dan Sitokinesis ‹#› ‹#› 2 9/28/2016 Benang-Benang mitotik (spindle): tidak terlihat Benang-Benang mitotik • Adalah organel mikrotubul yang mengatur pergerakan kromosom pada waktu pembelahan sel •Spindle muncul/timbul dari Sentrosom • Termasuk spindle mikrotubul dan aster • Beberapa spindle mikrotubul • Melekat pada kinetochores kromosom dan kromosom bergerak pada bidang metaphase ‹#› ‹#› Sitokinesis: • Pada sel tumbuhan, pada waktu sitokinesis • Pada sel hewan • Sitokinesis terjadi melalui proses yang dikenal sebagai proses pelipatan “cleavage”, membentuk cleavage furrow • Membentung bidang pembelahan sel ‹#› • Pada binary fission • Kromosom bakteri mengalami replikasi • Dua (2) anak kromosom masing-masing bergerak aktif Origin of replication 2 Replication continues. One copy of the origin is now at each end of the cell. Apa & bagaimana pengendalian siklus sel ? G1 checkpoint Cell wall E. coli cell 1 Chromosome replication begins. Soon thereafter, one copy of the origin moves rapidly toward the other end of the cell. ‹#› Two copies of origin Origin Plasma Membrane Bacterial Chromosome • Pengendali siklus sel : • Secara langsung dikendalikan dalam setiap tahapan, seperti siklus sebuah jam Origin Control system S G1 M 3 Replication finishes. The plasma membrane grows inward, and new cell wall is deposited. G2 M checkpoint G2 checkpoint 4 Two daughter cells result. ‹#› ‹#› 3 9/28/2016 Pengendalian siklus sel : pengendalian tingkat molekul. • Aktivitas cyclins and Cdks (Mitotic Protein Factor/MPF) • Berfluktuasi selama siklus sel • Ada dua (2) tipe Molekul Protein Pengatur siklus sel : • Cyclin dan Cyclin Dependent Kinase (CDk) disebut sebagai Mitotic Protein Factor/MPF ---------------- =Titik-titik pengendalian (Checkpoint) ‹#› Kehilangan kendali (Control) siklus sel ? menyebabkan Kanker Sel ‹#› A. Catatan yang perlu diingat : Sel anak, replikasi, kondensasi, sel somatik, diploid, sel gmet, haploi, kromosom, kromatin,Mitosis,Mitotik, Sitokinesis ! B. Tugas yang perlu dibahas : 1. Apa saja tujuan reproduksi sel ? 2. Apa persamaan & Perbedaan Mitosis & Meiosis ? 3. Jelaskan tiga (3) tahapan (Fase) & sub-fase siklus sel ? 4. Apa perbedaan sitokinesis pada sel Hewan & sel tumbuhan ? 5. Jelaskan sistem pengendalian siklus sel ? 6. Apa yang terjadi jika kehilangan kontrol siklus sel pada manusia, berikan contohnya ? • Contoh : Tumor payudara dapat berkembang dengan cara : • Mengirim sel kanker ke bagian lain dalam tubuh membentuk tumor sekunder. ‹#› ‹#› Banyak orang dapat masuk universitas, tapi belum, Tapi belum tentu bisa membuatnya berfikir. (Finley Peter Dunny) TERIMAKASIH 4